Understanding the Difference Between Structured and Unstructured Data

In the age of data-informed decision-making, distinguishing between structured and unstructured data is essential for optimal data management and processing strategies. Structured and unstructured data underpin various analytical workflows, from predictive models to customer insights. While structured data is organized into predefined schemas of rows and columns, unstructured data—encompassing formats such as text, images, and video—lacks such a structure, posing distinct challenges and opportunities.
What is Structured Data?
Structured data is highly organized, machine-readable data that follows a strict schema or data model, making it easy to search, analyze, and process data for both humans and artificial intelligence. Common formats include relational databases (e.g., SQL), CSV files, XML, and JSON, where data is systematically stored in rows and columns. This rigid structure enables efficient storage, retrieval, and analysis, playing a pivotal role in machine learning (ML), artificial intelligence (AI), and data visualization systems.
Structured data is essential for business intelligence and operational reporting, ensuring data readiness for AI and human workflows. This data enables timely insights, accurate analysis, and streamlined decision-making across your company by organizing information into consistent, reliable formats. The foundation of structured data not only improves operational efficiency and reporting precision but also supports scalability, allowing organizations to adapt seamlessly as data volumes and analytical needs expand.
Structured data consistently outputs high AI data quality by providing organized and labeled datasets, which are necessary for training accurate predictive models. For example, AI systems can rapidly process structured datasets such as sales figures, inventory metrics, or transaction logs to inform business decisions, leveraging structured data for accurate and scalable models.
What is Unstructured Data?
Unstructured data lacks a predefined format or schema, which can make searching, processing, and analyzing a greater challenge. There are diverse forms of unstructured data, such as text, image, audio, and social media content. This data is often stored in its raw format, which is not readily searchable or applicable without specialized tools. Because of these challenges, advanced techniques like Natural Language Processing (NLP), machine learning, and data mining are required to process and derive insights from unstructured data.
Because of its complexity, unstructured data creates challenges for AI data quality, as AI models need significant preprocessing, like tagging and organizing, to ensure unstructured data readiness for teams and further AI training. For instance, raw customer feedback on social media requires sentiment analysis and keyword extraction before AI can understand it, which can take much more time compared to structured data.
Despite these limitations and challenges, unstructured data is still incredibly valuable for gaining qualitative insights and uncovering deeper trends that structured data alone cannot reveal. With the proper techniques, businesses can harness unstructured data to drive innovation and improve customer experience.
What is the Difference Between Structured and Unstructured Data?
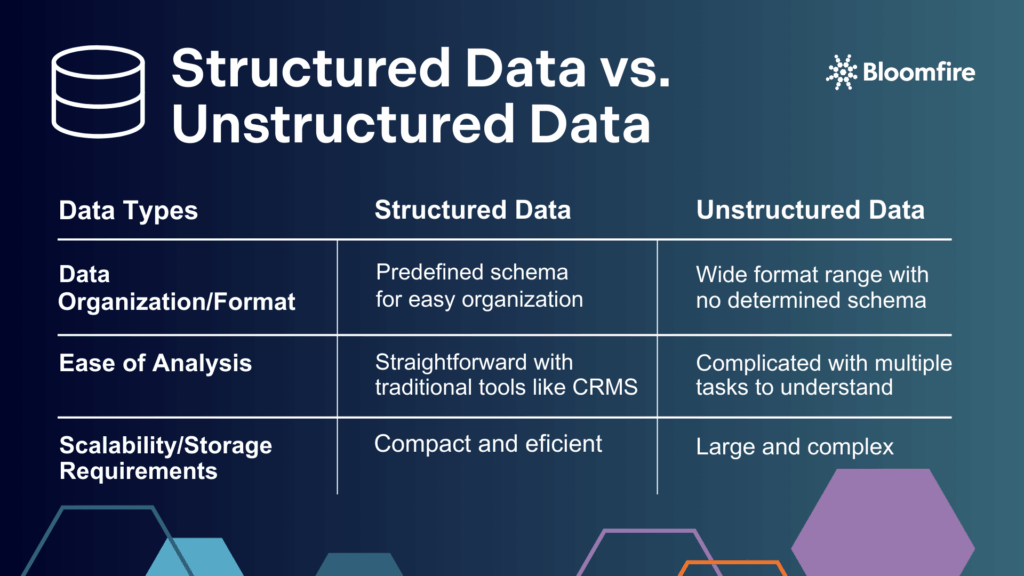
The key differences between structured and unstructured data are in data organization and format, ease of analysis and processing, and scalability and storage requirements.
For example, structured data can be easily understood and stored, whereas unstructured data might be complex to analyze and format. It’s important to understand the differences between these data types so you can use them effectively and efficiently.
1. Data Organization and Format
Structured data is organized in a predefined schema, typically stored in tables with rows and columns, allowing for predictable, consistent data storage. Relational databases like SQL, which are designed to organize data into tables, use this structure for easy data retrieval and querying.
Unstructured data, on the other hand, lacks this uniform organization. It can exist in a wide range of formats, from text to multimedia, which makes storage and retrieval more complex. Due to their flexibility, NoSQL databases and data lakes are typically used to store unstructured data, as NoSQL databases store non-tabular formats while data lakes store pure, raw data.
2. Ease of Analysis and Processing
Processing structured data using traditional tools like SQL and rule-based analytics is relatively straightforward. Its rigid format allows for efficient searching and querying, making it ideal for routine business tasks.
Unstructured data requires advanced techniques such as NLP, machine learning, and deep learning algorithms to extract insights. Processing unstructured data, like text documents or multimedia files, can involve complex tasks. Some tasks, like image recognition, sentiment analysis, or keyword extraction, require more computational power and sophisticated tools.
3. Scalability and Storage Requirements
Structured data is compact and efficient in storage, especially when schema constraints are consistent. However, its scalability can become limited as data volume grows.
Unstructured data demands larger storage systems, such as NoSQL databases or data lakes, to handle its variety and volume. These systems provide the necessary flexibility but introduce more complexity in managing data at scale.
Add the graphic: Structured Data vs. Unstructured Data
Leveraging Structured and Unstructured Data in Knowledge Management
Both structured and unstructured data play critical roles in knowledge management (KM). Structured data is vital to operational efficiency, allowing businesses to automate reporting, track performance, and process clean, organized data. On the other hand, unstructured data is essential for capturing qualitative insights—tacit knowledge, customer sentiment, and collaboration efforts.
Structured Data in Knowledge Management
Structured data is essential for capturing well-defined quantitative information within KM systems. Data stored in Customer Relationship Management (CRM) platforms, Enterprise Resource Planning systems (ERP), and content management systems (CMS) with applied metadata can be efficiently queried and analyzed. This structured approach makes such data highly reliable for routine business processes, automated reporting, and advanced analytics.
Key Applications Utilizing Structured Data in Knowledge Management
- Data Access and Decision-Making: Structured data (e.g., customer interactions, inventory, financial transactions) is easily accessed from databases to inform business decisions and refine processes.
- Trend Analysis and Reporting: Businesses use structured data for trend analysis and performance reporting.
- Automation and Predictive Analytics: Structured data powers AI models to automate tasks such as generating reports, managing workflows, and predicting outcomes.
- Performance Tracking: Sales figures and inventory data are automatically processed and displayed in dashboards, helping decision-makers track business performance.
Unstructured Data in Knowledge Management
Unstructured data captures the tacit knowledge and human experiences essential for innovation and decision-making. In KM, advanced tools like text mining, NLP, and machine learning help analyze this data, providing valuable insights into customer sentiment, market trends, and internal collaboration.
Key Applications Using Unstructured Data in Knowledge Management
- Tacit Knowledge Capture: Unstructured data (e.g., email correspondence, meeting notes, video interviews) stores valuable human insights and experiences, enriching AI models with nuanced, real-world data.
- Document and Multimedia Management: KM systems organize vast amounts of documents, research papers, and multimedia content, providing accessibility through advanced search features.
- Insight Mining with NLP and AI: Tools like NLP and machine learning analyze unstructured data (e.g., customer feedback) to extract sentiment and market trends for improved decision-making.
- Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing: Unstructured data (e.g., project reports and chat logs) enhances collaboration across teams through platforms like wikis, forums, and internal communication tools.
Integrating Structured and Unstructured Data in Knowledge Management
A modern knowledge management system (KMS) often combines structured and unstructured data to deliver more comprehensive insights. For example, a single search query could retrieve structured data (e.g., customer satisfaction scores) alongside unstructured data (e.g., customer reviews or emails), enriching the decision-making process.
Utilizing structured and unstructured data together can help your company succeed. Healthcare organizations use structured data, like patient records, alongside unstructured data from medical imaging or patient feedback to improve patient outcomes. Similarly, retailers analyze unstructured customer reviews to complement structured sales data, identifying trends and preferences that inform marketing and inventory decisions. As unstructured data now comprises over 80% to 90% of all generated information, businesses must implement advanced techniques to harness its potential while maintaining efficient structured data management.
AI models also benefit from this integration. Structured data, like sales figures, trains predictive models, while unstructured data, such as support tickets, can reveal recurring issues. These data types provide a fuller understanding of customer behavior, helping businesses improve products, services, and customer satisfaction.
How Enterprise Intelligence Overhauls Structured and Unstructured Data Integration
Enterprise Intelligence (EI) turns company knowledge into measurable business value, combining business intelligence, enterprise search, and knowledge management into one dynamic knowledge ecosystem. Structured and unstructured data are elevated in Enterprise Intelligence. With the use of AI, both data types are automated, updated, and enriched so they can easily turn into context-aware, actionable insights.
Structured Data in Enterprise Intelligence
Enterprise Intelligence rapidly processes structured data using advanced AI technologies, transforming it into a unified semantic layer. The platform serves as a foundation for enhanced AI learning, analytic reporting, and real-time decision making. This unified data layer makes structured information easily accessible and actionable by delivering predictive reporting and analytics, ensuring that all data remains relevant and meaningful. Through continuous AI training and automation, Enterprise Intelligence actively updates and maintains your data, converting static structured data points into dynamic, insightful information.
As a result, your organization gains timely, real-time insights that empower smarter decisions, improve operational efficiency, and deliver proactive approaches to business challenges. By leveraging Enterprise Intelligence, you ensure that your structured data is not only consistently accurate and readable, but also evolving into a strategic asset driving innovation and growth.
Unstructured Data in Enterprise Intelligence
Unstructured data can be seamlessly integrated into Enterprise Intelligence systems through AI-driven processes that connect directly to raw data sources. These AI models automatically cleanse, organize, and enrich unstructured data, transforming it into high-quality, easily interpretable insights.
Enterprise Intelligence plays a crucial role in supporting the information architecture process, which organizations use to organize, structure, and present information in ways that make it simple to find, understand, and use. By applying AI-powered automation, Enterprise Intelligence brings greater structure to unstructured data, extracting key information efficiently and enabling businesses to build a clear, intuitive information architecture.
With Enterprise Intelligence, unstructured data unlocks valuable insights that would otherwise remain hidden in raw, disorganized formats. It enables organizations to analyze and interpret complex information from diverse sources quickly, ultimately enhancing decision-making by providing accurate and relevant data in an easily accessible form. Enterprise Intelligence will help your unstructured data drive greater efficiency, innovation, and competitive advantage across different business operations.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How do companies turn unstructured data into actionable insights?
To transform unstructured data into actionable insights, companies must rely on essential algorithms and modern data analytics tools that are designed to analyze and understand unstructured data types. Start by collecting unstructured information from sources like social media and customer feedback from your respective data tool, so the information can be analyzed, visualized, and turned into actionable insights.
Q: How do businesses decide when to use structured or unstructured data?
Companies will choose between structured and unstructured data depending on their use case and business objective. Structured data is favored when companies require quick, standardized, and highly accurate analytics for things like financial statements or inventory tracking. In contrast, unstructured data becomes valuable when understanding broad, abstract patterns with qualitative insights from customer reviews or other media, which can have multiple different file types.
Q: What are the main advantages and disadvantages of each data type?
Structured data is incredibly beneficial with its ease of storage, search, and analysis usage, but is also reliant on specific formats, making it difficult to capture qualitative data that many companies need. Unstructured data, on the other hand, is capable of capturing relevant, qualitative data from many different formats that can evolve into actionable insights. Unfortunately, unstructured data is difficult to store while requiring advanced expertise and technologies to analyze the data, posing greater challenges in extracting reliable, scalable, and quantitative knowledge.
Q: Does AI use structured or unstructured data?
AI leverages both structured data and unstructured data according to the specified task and desired outcome. Structured data is efficiently processed, analyzed, and fed into AI algorithms like traditional machine learning models for quick insights, predictions, and categorization tasks. AI harnesses technologies like natural language processing (NLP), computer vision, and deep learning to extract meaning, patterns, and insights from unstructured data, enabling tasks like sentiment analysis, image recognition, and content generation.
Leveraging Structured and Unstructured Data for Comprehensive Insights
Understanding the difference between structured and unstructured data is critical for maximizing their potential in data analytics, AI, and Knowledge Management. Dr. Anthony Rhem, a leading authority in knowledge management, advises that businesses utilize both data types to support AI model accuracy and decision-making. He stresses that integrating structured and unstructured data enables companies to capture comprehensive insights and improve operational efficiency. To remain competitive in today’s data-driven world, organizations must combine structured and unstructured data, using advanced AI tools and techniques to unlock their data’s full potential. Proper data readiness for AI is essential to successfully implementing these technologies, enabling businesses to make more informed decisions and fostering continuous innovation.

How Knowledge Management Enhances the Decision-Making Process of Organizations

How You Can Use Knowledge Management to Finally Achieve Operational Excellence

Knowledge Management History: Why Businesses Took 50 Years to Adopt It
Estimate the Value of Your Knowledge Assets
Use this calculator to see how enterprise intelligence can impact your bottom line. Choose areas of focus, and see tailored calculations that will give you a tangible ROI.

Take a self guided Tour
See Bloomfire in action across several potential configurations. Imagine the potential of your team when they stop searching and start finding critical knowledge.