What Is Knowledge Management? A Complete Guide
Knowledge Management (KM) is a systematic approach that empowers organizations to capture, organize, and leverage knowledge, enhancing productivity and decision-making. It involves identifying, generating, storing, and distributing knowledge assets, ensuring that employees can access and apply the necessary information when required.
Clear knowledge management allows organizations to effectively utilize their intellectual capital, fostering innovation, promoting collaboration, and enhancing overall performance. This comprehensive guide offers an in-depth look at what is knowledge management, covering its different types, processes, benefits, challenges, tools, strategies, and real-world applications.
A Brief History of Knowledge Management
Knowledge management isn’t a newfangled concept. Humans have always sought to capture and share what they know, from ancient oral traditions to the libraries of Alexandria. However, the formalization of knowledge management as a discipline took root in the late 20th century.
As businesses grappled with the explosion of information and the increasing complexity of their operations, they began to recognize the strategic importance of leveraging their collective knowledge. Early efforts focused on codifying best practices and creating databases to store information.
The evolution of knowledge management continued with the rise of the internet and collaborative technologies. Suddenly, sharing and accessing information became vastly easier, and the focus shifted from simply storing knowledge to fostering its creation and dissemination. This ushered in an era of intranets, wikis, and online communities where employees could connect, learn, and contribute in real time.
Today, knowledge management is about creating a dynamic ecosystem where information flows freely, empowering organizations to adapt, innovate, and thrive. It’s less about static repositories and more about building a culture of continuous learning and knowledge sharing.
Why Knowledge Management Is Important
Knowledge Management is crucial for organizations because it enhances decision-making, boosts efficiency, fosters innovation, and promotes collaboration. IDC reports that knowledge workers spend approximately 2.5 hours daily, or 30% of their work, searching for information.
By systematically capturing, organizing, and sharing knowledge, KM ensures that valuable information is accessible when needed. It not only reduces the time but also enables employees to make informed decisions quickly. It also helps preserve institutional knowledge, supporting continuity and long-term success.
Additionally, knowledge management encourages a culture of continuous learning and knowledge sharing, driving innovation and keeping organizations competitive. Gallup reports that improvements in employee engagement can lead to an 18% increase in productivity and a 23% increase in profitability, underscoring the significant impact KM can have. Ultimately, effective knowledge management leads to improved organizational performance and growth.
The ROI of Knowledge Management
Calculating the return on investment (ROI) of knowledge management can be complex, as it involves both tangible and intangible benefits. Tangible ROI can be measured through increased efficiency, reduced training time, and decreased support costs.
For example, a well-organized knowledge base can empower employees to find answers quickly, minimizing downtime and boosting productivity. Additionally, streamlined onboarding processes and reduced errors from readily available information contribute to measurable cost savings.
Discover Your Potential ROI
Try Bloomfire’s free KM ROI calculator and see how much your organization could save.
Calculate Your KM ROI
However, the true value of KM often lies in its intangible returns. These include improved decision-making, enhanced innovation, and stronger organizational learning. Through streamlined knowledge sharing and collaboration, KM fosters a culture of continuous improvement, leading to better products, services, and customer experiences. Furthermore, it strengthens employee retention and morale by empowering individuals with the information they need to succeed.
What Is the Purpose of Knowledge Management?
The purpose of knowledge management is to systematically handle and utilize the knowledge within an organization to enhance its efficiency, productivity, and overall performance. By implementing KM, organizations aim to:
- Facilitate decision-making: KM provides a structured approach to capturing and organizing valuable information, ensuring employees access the right knowledge at the right time.
- Improve efficiency: A robust knowledge management system centralizes and standardizes knowledge to reduce redundancies and streamline processes. Employees spend less time searching for information and more time executing tasks effectively.
- Promote innovation: KM fosters a culture of continuous learning and knowledge sharing. By facilitating the exchange of ideas and experiences, organizations can drive innovation and stay competitive in their respective industries.
- Enhance collaboration: KM tools and practices encourage collaboration across departments and teams. By breaking down information silos and enabling seamless knowledge sharing, organizations can leverage the collective expertise of their workforce.
- Preserve institutional knowledge: KM helps capture and retain critical knowledge, especially from departing employees, ensuring that valuable insights and expertise are preserved over time.
- Support learning and development: Knowledge management contributes to employee growth by providing access to training materials, best practices, and lessons learned.
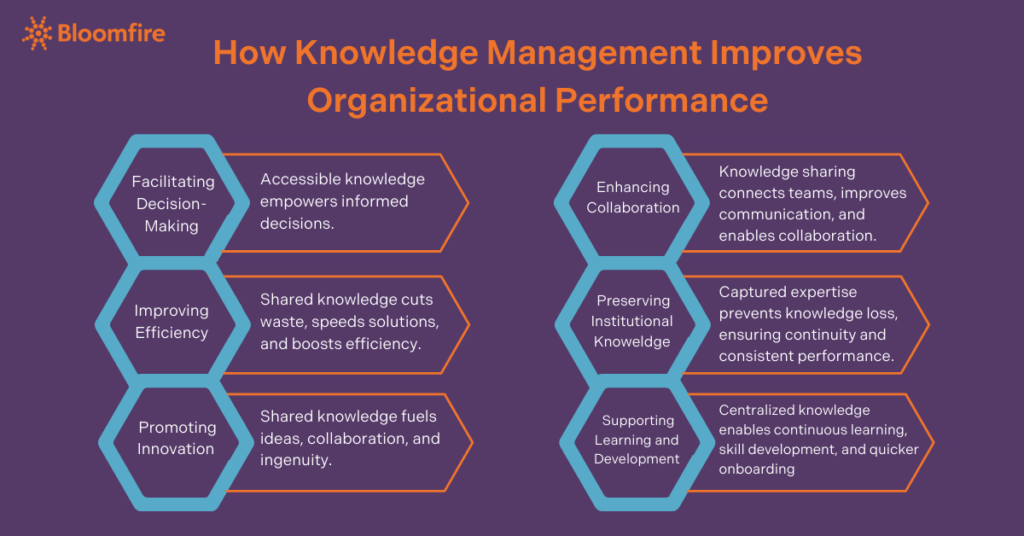
Components of Knowledge Management
Several core components are essential for effectively creating, sharing, and utilizing organizational knowledge. These elements interweave to form a robust KM system, although the breakdown may vary. While the precise breakdown can vary, here are the core components generally recognized as a key part of an organization’s knowledge management framework:
- People: The heart of KM. They are the creators, sharers, and users of knowledge, including those primarily responsible for maintaining the system. This includes fostering a culture that encourages collaboration and knowledge sharing.
- Processes: Structured activities that enable the flow of knowledge define the processes component, encompassing capture, storage, and dissemination. These procedures ensure that knowledge is organized, accessible, and applicable throughout the organization.
- Content: Content in knowledge management encompasses all forms of information, from documented procedures to the tacit expertise held by individuals. It is the raw material that knowledge management systems organize, share, and apply.
- Technology: Tools like knowledge repositories and collaboration platforms enable knowledge management processes. The IT infrastructure supporting these systems allows for efficient storage, retrieval, and information sharing.
- Strategy: A well-defined strategy aligns knowledge management initiatives with overarching organizational goals, ensuring knowledge is leveraged to achieve specific objectives. It provides a roadmap for creating, sharing, and utilizing knowledge to drive business value.
- Governance: Effective knowledge management relies on a structured framework of rules and guidelines to ensure proper use and maintain the integrity of information. Governance provides oversight and direction, guaranteeing that knowledge is managed in alignment with organizational goals.
Power Move: A knowledge management system like Bloomfire provides a platform that supports all components of KM. It offers tools (technology) for capturing and organizing explicit knowledge (content) in repositories while facilitating collaboration and knowledge sharing (processes) among individuals (people).
Types of Knowledge
Knowledge management is a multifaceted concept incorporating various strategies and methodologies to manage and utilize knowledge effectively. Understanding the different types of knowledge can enhance operational efficiency and decision-making processes. This section delves into three key categories of knowledge management: explicit versus implicit versus tacit knowledge, structured versus unstructured knowledge, and internal versus external knowledge.
Explicit, Implicit, and Tacit Knowledge
Explicit knowledge is the codified information that can be easily transferred through formal documentation such as manuals, reports, or databases. It’s tangible and can be explicitly articulated, shared, and communicated. Implicit knowledge is not explicitly stated but is implied or understood. On the other hand, tacit knowledge, deeply rooted in individuals’ minds, is based on their experiences, insights, and expertise. This type of knowledge is challenging to articulate and transfer due to its personal context and intuitive nature.
Structured and Unstructured Knowledge
Knowledge and data can be structured or unstructured, depending on how the information is organized and formatted. Structured knowledge is organized and stored in a predefined format, making it easily searchable and accessible. It comprises well-defined processes, procedures, and models. Conversely, unstructured knowledge needs a formalized structure or framework. It often exists in informal conversations, brainstorming sessions, or personal notes, making it more challenging to capture and retrieve.
Internal and External Knowledge
Internal knowledge is generated, shared, and utilized within an organization and includes proprietary data, best practices, and lessons learned from past experiences. Alternatively, external knowledge is derived from sources outside the organization, such as industry reports, market research, or insights from external experts. External knowledge can provide fresh perspectives and keep organizations updated with industry trends and advancements.
Benefits of Knowledge Management
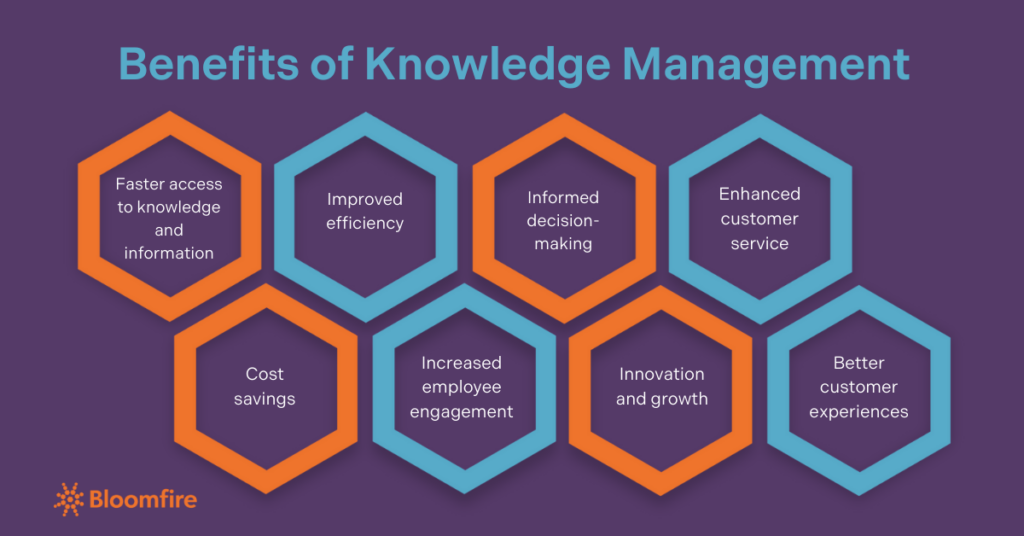
Knowledge management offers numerous advantages, enhancing organizational performance and growth. By systematically capturing and organizing information, organizations can streamline processes, foster innovation, and improve decision-making. The benefits of knowledge management in business extend to faster access to knowledge and information, improved efficiency, and enhanced customer service. Key benefits include:
- Faster access to knowledge and information
- Improved efficiency
- Informed decision-making
- Enhanced customer service
- Cost savings
- Increased employee engagement
- Innovation and growth
- Better customer experiences
Power Move: Organizations can further maximize the advantages of knowledge management by expanding their intellectual assets into enterprise intelligence. This approach grows into an internal network comprised of a knowledge-sharing culture, analytics, and tailored insights.
Challenges of Knowledge Management
Implementing and maintaining effective knowledge management (KM) systems presents several significant challenges for organizations. These challenges range from fostering a culture of knowledge sharing to selecting and integrating appropriate technologies and often include overcoming employee resistance to change. Here are some of the key hurdles:
- Capturing tacit knowledge: One of the most challenging tasks is capturing tacit knowledge, the expertise and insights that reside in individuals’ minds. Not only are they difficult to articulate and codify into shareable formats, but individuals may not even be consciously aware of the knowledge they possess.
- Resistance to change: Adopting new knowledge management tools and processes often disrupts established workflows, leading to employee reluctance to abandon familiar habits. Consequently, this resistance hinders the successful implementation and utilization of the KM system, as employees may avoid or underutilize it.
- Lack of a knowledge-sharing culture: If employees are unwilling to share their expertise, vital knowledge remains siloed, limiting organizational learning and innovation. Without a culture prioritizing collaboration, even the most robust KM systems will fail to capture and disseminate valuable insights.
- Information overload: A deluge of data and information makes locating and utilizing relevant knowledge difficult. In addition, the sheer volume of information can overwhelm users, rendering knowledge management systems less effective if they lack robust filtering and organization mechanisms.
- Keeping knowledge updated: Because knowledge evolves constantly, maintaining accurate and relevant information within a system requires ongoing effort and resources. Without this vigilance, the knowledge base quickly becomes outdated and unreliable, diminishing its value.
- Ensuring knowledge trustworthiness: Varied contributors and evolving information require robust verification processes to maintain accuracy and reliability within knowledge repositories. Without such safeguards, the credibility of the entire knowledge management system can be compromised, leading to flawed decisions.
While these challenges may create a roadblock to your KM implementation, there are proven ways to address them successfully. For example, you should start fostering a culture that prioritizes knowledge sharing and collaboration, as well as incentivizing employees to contribute and actively participate.
Also, implement robust technology solutions to streamline information capture, storage, and retrieval to ensure data accuracy and accessibility. Consider options with strong AI capabilities, not just because it’s a fad but because it is in demand. In fact, 38% of knowledge management teams cite AI to recommend content or knowledge assets as a top essential technology. In addition, secure strong leadership support and demonstrate the tangible benefits of KM through measurable metrics to overcome resistance and maintain momentum.
Knowledge Management Process
Embarking on the knowledge management journey involves several key stages. Each stage represents a critical step in building a robust and effective knowledge management process. This involves implementing tools and creating a holistic approach that aligns with your organization’s objectives and culture. Key stages include:
- Evaluating current knowledge infrastructure
- Defining knowledge management goals and selecting KM leaders
- Developing your knowledge management strategy
- Selecting the right knowledge management tool
- Structuring your knowledge management system
- Implementing the knowledge management system
- Integrating knowledge management into daily operations
- Managing and enhancing the knowledge management system
- Iterative improvement and adaptation
This structured approach ensures a dynamic and valuable knowledge management system that adapts to the evolving needs of your organization. Furthermore, it fosters a culture of continuous learning and knowledge sharing, empowering employees to contribute and access information efficiently.
Knowledge Management Tools
The world of KM is extensive, and the tools are varied. Therefore, a strategic approach is essential for selecting solutions that align with specific organizational needs. Let’s take a closer look at the existing types of knowledge management tools:
- Knowledge Bases: Centralized locations where organizational knowledge can be easily stored, organized, and accessed. Platforms like Bloomfire excel at turning information chaos into organized brilliance.
- Document Management Systems: Efficient storage, retrieval, and organization of diverse documents. These systems provide centralized repositories where documents can be stored, viewed, and organized, addressing document sprawl and duplication challenges.
- Record Management Systems: Ensure records remain unchanged, tamper-proof, and easily traceable. These systems preserve the integrity of vast amounts of records while ensuring accessibility.
- Content Management Systems: Efficiently manage and update external-facing content. Platforms like WordPress, Joomla, and Drupal help ensure a company’s public image remains updated, consistent, and engaging while also playing a vital role in KM by containing essential organizational knowledge.
Successful organizations recognize that knowledge management tools are integral to fostering a culture of continuous learning and information sharing. Implementing the right platforms and technologies empowers employees to utilize crucial knowledge, driving innovation and efficiency.
Knowledge Management Use Cases
Knowledge management can be applied across various industries and functions, demonstrating its versatility and value. Organizations of all sizes, from startups to multinational corporations, can benefit from implementing effective KM strategies. These strategies improve operational efficiency, enhance customer service, and promote innovation in diverse sectors. Here are some key use cases:

1. General Knowledge Management
Implementing knowledge management systems helps organizations systematically capture, store, and distribute knowledge. This ensures employees have easy access to the information they need, enhancing overall productivity and efficiency. Furthermore, fostering a knowledge-sharing culture through these systems strengthens collaboration and drives innovation.
2. Research & Insights
Knowledge management facilitates collecting and disseminating research findings and insights. By providing a centralized repository of information, organizations can drive innovation and make data-driven decisions more effectively. This process also ensures that valuable expertise is preserved and accessible to all relevant stakeholders.
3. Customer Success
Customer success teams use KM systems to access a centralized repository of information, enabling them to provide quick and accurate responses to customer inquiries. This improves customer satisfaction and reduces resolution times. Additionally, it ensures consistent messaging and best practices across all customer interactions.
4. Sales Enablement
Knowledge management supports sales teams by centralizing product information, marketing materials, and customer insights. This enables more effective sales strategies and targeted marketing campaigns, ultimately driving revenue growth. Readily available competitor intelligence and best-practice sales playbooks allow sales representatives to respond quickly to market changes and close deals more efficiently.
5. Knowledge Sharing
Knowledge management promotes a culture of knowledge sharing within organizations. Employees can collaborate more effectively and leverage collective expertise to solve problems by facilitating the exchange of ideas and best practices. This enhanced collaboration strengthens organizational learning and empowers teams to innovate.
6. Enterprise Intranet
An enterprise intranet powered by knowledge management can be a central hub for company-wide information. This improves communication, ensures consistency, and provides employees easy access to policies, procedures, and essential updates.
7. Employee Collaboration
Knowledge management tools enhance employee collaboration by providing platforms for sharing documents, ideas, and feedback. This encourages teamwork and ensures everyone is on the same page, leading to better project outcomes. In addition, it fosters a collaborative environment where employees can share expertise and contribute to a shared knowledge base.
8. Corporate Wiki
A corporate wiki allows employees to create and edit a centralized knowledge base. This dynamic resource grows with the organization, ensuring valuable knowledge is documented and easily accessible for future reference. It cultivates collaborative knowledge sharing, reducing information and knowledge silos and promoting a more informed workforce.
These use cases highlight the broad applicability of knowledge management, showcasing how organizations across different sectors can benefit from effective knowledge management practices. Moreover, they demonstrate that strategic knowledge management initiatives can yield measurable improvements in operational efficiency, innovation, and overall organizational performance.
Knowledge Management Trends and Practices in 2025
The knowledge management landscape is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements and shifting workplace dynamics. In 2025, organizations realize the critical importance of treating data as a dynamic asset. Leaders continue leveraging tools like AI to streamline workflows and provide consumer-grade user experiences. With these advancements, it’s crucial to understand new shifts and progressions in handling corporate knowledge.
The following are key trends and practices in knowledge management that your organization should keep up with.
- Treating corporate data as a dynamic asset and developing new frameworks to evaluate its impact.
- Maximizing growth through productivity by leveraging automation and streamlining workflows.
- Focusing on data cleanliness for AI success by investing in data-cleaning tools and standardizing data formats.
- Delivering consumer-grade experiences for enterprise users by adopting platforms that leverage AI and ensure seamless accessibility of information.
- Proving the value of technology investments by tying them to measurable outcomes and creating data-driven business cases.
The future of knowledge management hinges on treating data as a living, valuable asset, prioritizing its quality, and delivering it through intuitive, user-friendly platforms. Simultaneously, organizations must leverage automation to boost productivity and demonstrate the tangible ROI from their knowledge management initiatives. Ultimately, these trends point toward a more agile, data-driven, and user-centric approach to knowledge management.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary goal of knowledge management?
Knowledge management aims to improve organizational performance by effectively capturing, organizing, and sharing knowledge to improve efficiency and decision-making. It intends to make relevant information accessible to the right people at the right time, fostering collaboration and innovation. This process empowers employees to leverage collective intelligence.
How does knowledge management improve productivity?
Effective knowledge management provides accessible and organized information, allowing employees to quickly find needed resources and reduce time spent searching. As a result, they have more time to focus on high-level tasks. In addition, streamlined workflows and automated processes facilitated by effective knowledge management minimize repetitive tasks.
How can knowledge management be improved in an organization?
Organizations can enhance knowledge management by implementing a user-friendly KM platform with robust search functionalities. Additionally, they can invest in data quality initiatives, such as standardization and cleaning, to ensure reliable insights for decision-making. Finally, they can a knowledge-sharing culture through training and collaboration tools should be fostered to encourage continuous learning and innovation.
Wrapping Up the Importance of Knowledge Management
Knowledge management is vital for organizations to enhance productivity, foster innovation, and improve decision-making. A robust knowledge management process enables organizations to leverage their intellectual capital effectively, driving growth and maintaining a competitive edge. Embracing KM practices ensures that valuable knowledge is preserved and utilized, benefiting employees and the organization.
Note: This post was expanded and updated in March 2025.
Master KM in One Space!
Dive deeper into knowledge management strategies and practices.
Get Our Guide

7 Proven Strategies on How to Improve Collaboration in an Organization

The Importance of Knowledge Management in Banking
Start working smarter with Bloomfire
See how Bloomfire helps companies find information, create insights, and maximize value of their most important knowledge.

Take a self guided Tour
See Bloomfire in action across several potential configurations. Imagine the potential of your team when they stop searching and start finding critical knowledge.

