What Is Business Intelligence? A Complete Guide

Business Intelligence (BI) is a comprehensive framework that enables organizations to make data-driven decisions and gain a competitive edge. BI tools and techniques transform raw data into valuable insights, powering smart decision-making. As one of the three pillars of Enterprise Intelligence, BI plays a critical role in providing the data and insights necessary for an organization to understand its past and present, enabling it to strategize for the future.
Self-service BI platforms offer an intuitive interface, enabling users to get started quickly and easily. Marketing teams can analyze social media performance, sales teams can track lead generation metrics, and executives can monitor key performance indicators without needing a data scientist.
Below, you’ll learn about business intelligence definition, how BI works, why it’s an essential pillar of Enterprise Intelligence, and how it impacts your bottom line.
What Is Business Intelligence (BI)?
Business intelligence combines technological processes that collect, manage, and analyze organizational data to provide actionable insights. This analysis yields insights that shape business strategies and operations.
The system blends business analytics, data mining, data visualization, data tools, infrastructure, and best practices. It provides complete business metrics almost instantly. BI helps companies make informed decisions, spot areas needing improvement, and stay ahead of competitors. It removes guesswork and gut feelings from significant business decisions. Plus, it displays all your critical business data in one easy-to-understand location.
How Business Intelligence Fits Into Enterprise Intelligence
The global business intelligence market is projected to reach $55.48 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 10.1%. To stay competitive, your organization needs to leverage the power of data effectively.
In the case of large, complex organizations, enterprise business intelligence is highly essential. The system supports multiple departments, handles massive data volumes, and meets strict governance requirements. This ground application works with sprawling tech stacks and cross-functional teams. However, to ensure organizational success, you must transition from merely business intelligence to Enterprise Intelligence.
Business intelligence is one of the three pillars of Enterprise Intelligence. The other two are Enterprise Search (ES) and Knowledge Management (KM). All three work together to create a dynamic knowledge ecosystem.
While BI analyzes structured data to drive decision-making, Enterprise Search allows you to retrieve information from across the entire organization, and Knowledge Management captures and organizes all institutional knowledge, including unstructured data like documents and videos. This holistic approach ensures that all forms of data are continuously updated and easily accessible, providing a complete and clear picture of your business.
The Main Advantage of Enterprise Business Intelligence
Enterprise BI helps organizations improve productivity by optimizing data management and analytics. Teams that keep data collection and analytics isolated create information silos. These silos risk causing inefficiencies and redundancies.
Enterprise Intelligence extends beyond traditional BI capabilities. The system provides complete insights into all business areas, including process analyses that conventional BI tools often miss. Traditional BI analyzes historical data from limited sources. On the other hand, Enterprise Intelligence seamlessly integrates data from multiple sources throughout the organization.
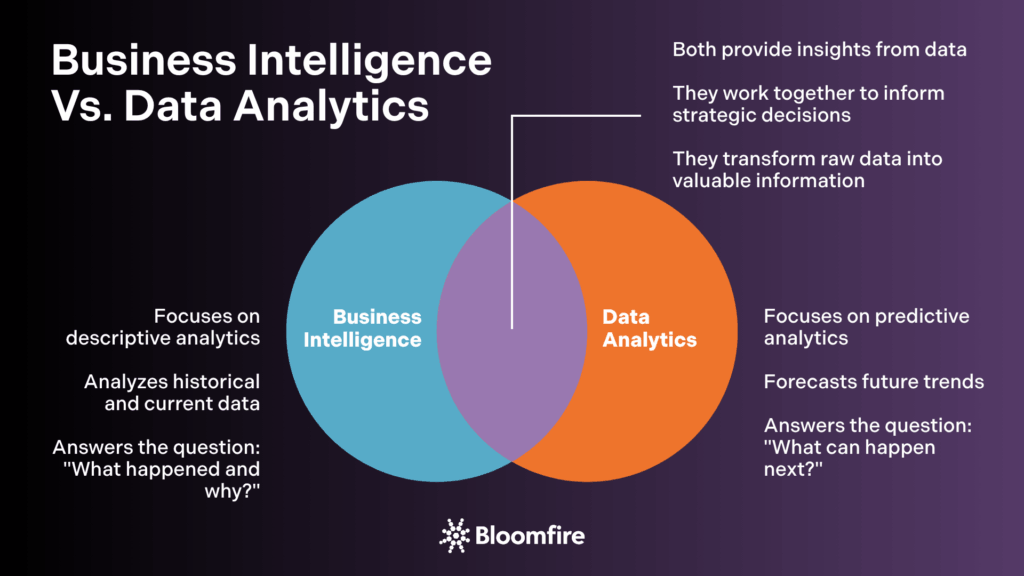
Business Intelligence vs. Data Analytics: Key Differences
BI and data analytics serve different functions despite their interchangeable use. BI focuses on descriptive analytics, which summarize historical and current data. These summaries show past and current events.
Data analytics involves technical processes of mining, cleaning, transforming, and managing data. Data scientists use advanced statistics and predictive analytics to find patterns and forecast future trends.
BI analyzes current operational data to guide decision-making. Business analytics explores deeper predictive insights for future growth. Simply put, BI asks “what happened and why,” while data analytics explores “why did this happen and what can happen next”.
How Business Intelligence Works
Business intelligence transforms raw data into actionable insights through a well-defined workflow. As a component of Enterprise Intelligence, influencing its core principles, it operates through five connected stages. These stages create a continuous cycle of information processing and use. Each step is crucial for transforming complex data into a clear, actionable story for a business.
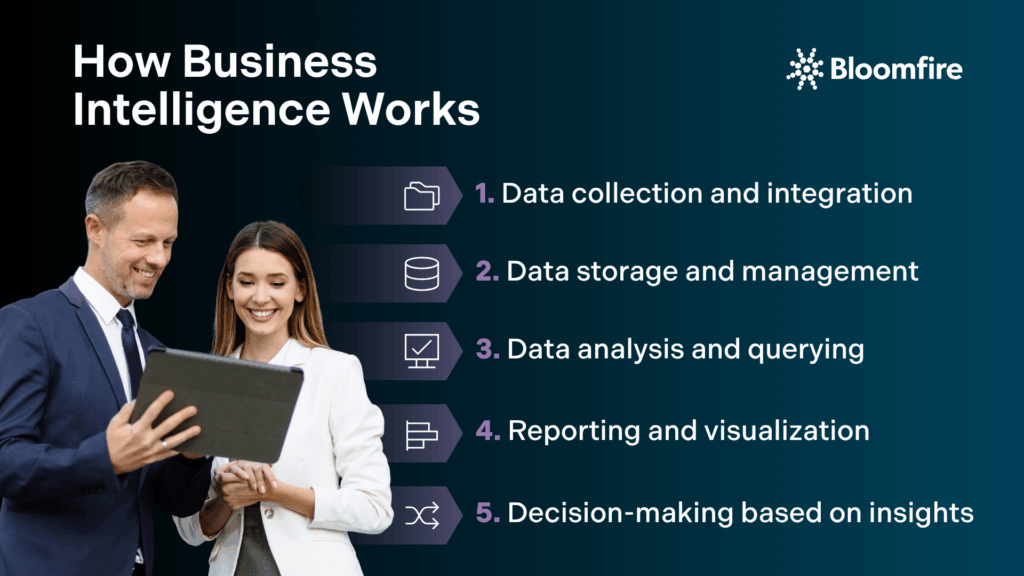
1. Data collection and integration
Your BI trip begins with gathering data from multiple sources, both internal and external. Business intelligence tools utilize the extract, transform, and load (ETL) method to integrate structured and unstructured data from various systems.
Modern approaches also use ELT. This loads raw data directly into warehouses before transformation. The integration eliminates data silos and brings together information from different systems, including customer relationship management (CRM), enterprise resource planning (ERP), social media, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices, to create a unified view.
2. Data storage and management
Data is moved to centralized repositories, such as data warehouses, data lakes, or cloud-based solutions, after collection. These specialized databases organize information in a business-friendly format, making analysis more accessible.
Data warehouses are the foundations of BI. They act as a single source of truth that gives a comprehensive view of your organization’s data. Modern systems employ advanced security measures to safeguard confidential information while maintaining accessibility and usability.
3. Data analysis and querying
Stored data undergoes examination through various analytical techniques at this stage. BI tools utilize data mining to analyze information, identifying patterns and outliers. These show insights about your current business state.
Online analytical processing (OLAP) enables multidimensional analysis. You can explore data from different angles simultaneously. Raw numbers transform into meaningful information that reveals trends, anomalies, and relationships.
4. Reporting and visualization
Visualization turns complex datasets into understandable formats that tell a data story. Business intelligence reporting uses interactive dashboards, charts, graphs, and maps. These make findings easier to understand and share.
These visual tools help you see your business’s current state. Research shows that humans process visual information faster. This makes visualization significant for quick data interpretation.
5. Decision-making based on insights
BI exists to enable informed decision-making. Your company can move quickly from insights to action with current and historical data in context. Companies that use business intelligence are 23 times more likely to acquire customers and 19 times more likely to be profitable. These informed decisions help eliminate inefficiencies, adapt to market changes, address supply problems, and resolve customer issues.
Types of Business Intelligence Tools and Techniques
Modern business intelligence systems offer a range of features tailored to meet specific organizational needs. These systems serve as the backbone of Enterprise Intelligence, addressing various aspects of data analysis and decision support.

1. Self-service BI
Self-service business intelligence makes data available to everyone. Non-technical users can analyze information and create visualizations independently without IT help. This approach provides users with freedom while maintaining control over data usage.
Employees from all departments can explore data wherever it takes them. This creates a true data culture and supports flexible analysis. Good self-service tools help bridge the data literacy gap by providing an easy-to-use interface that guides users toward more effective analytical practices.
2. Real-time BI
Real-time business intelligence provides up-to-the-minute data analysis on operations, revealing what’s happening at any given moment. Companies can adapt quickly to market changes and make almost instant decisions.
Businesses identify trends promptly by analyzing incoming data. They can create alert systems for exceptions and generate current reports. This speed gives them a major edge over competitors who use older information.
3. Mobile and embedded BI
Mobile BI puts dashboards and analytics on smartphones and tablets, which frees users from their desks. Embedded BI seamlessly integrates analytics with existing applications and workflows. Users don’t need to switch between systems.
Organizations can provide branded customer-facing reports with fully customizable interfaces. Analytics adoption increases when users see insights in familiar contexts.
4. Predictive and prescriptive analytics
Predictive analytics looks into future outcomes based on past data. It answers “What might happen?” by finding patterns. Users often apply it to content recommendations, inventory forecasting, and risk assessment.
Prescriptive analytics goes further by suggesting specific actions for the best results. This advanced method utilizes AI and machine learning to deliver valuable insights and recommendations across various sectors, including healthcare, finance, and retail.
5. Collaborative and location intelligence
Location intelligence boosts BI by adding geospatial context. It creates powerful “where” views that show routes, patterns, and spatial relationships. Businesses use mapping visualizations to improve their marketing, logistics, risk assessment, and resource allocation.
According to a report by Precedence Research, the global location intelligence market was valued at $22.79 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach $68.22 billion by 2034. It’s also projected to have an impressive Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 11.59% during that period.
6. Open-source and cloud-based BI tools
Open-source BI platforms like Apache Superset and Metabase offer enterprise-grade analytics while keeping their source code freely available for customization. These tools have core BI features at lower costs than proprietary solutions.
Cloud-based BI eliminates the need for expensive on-site hardware by offering subscription models that scale with business needs. Users can access data from anywhere while providers handle infrastructure management.
Benefits and Value of Business Intelligence
Business intelligence implementation delivers measurable advantages at every organizational level. BI transforms raw data into strategic value that affects your bottom line. Organizations can uncover new opportunities through robust data analysis. Ultimately, these insights provide a competitive edge and drive sustainable growth.

1. Improved decision-making
Real-time data from BI tools supports informed and strategic decisions. The quality of decisions also improves because reduced uncertainty and risk align with strategic objectives, rather than being confined to departmental silos.
2. Operational efficiency and cost savings
Your business can spot hidden inefficiencies through BI. Companies can apply specific improvements to optimize resource use by analyzing operational data. Retailers who use BI can cut inventory costs by up to 15% while improving delivery times. On top of that, automated reporting and analysis save time and cut down on human errors.
To cite an instance, companies using BI solutions have reported:
- 20% lower staff costs and 40% faster processes
- Major reductions in maintenance costs through predictive analysis
- Streamlined operations by combining data from different systems
- Customer insights and personalization
BI goes beyond simple analytics to help understand customer behavior and priorities. Businesses can create individual-specific offerings based on specific traits through detailed analysis of customer data. This becomes especially valuable when you have personalized emails generating 40% more revenue than average players.
Additionally, personalization can lift revenues by 5% to 15%. These insights help identify recurring issues, anticipate needs, and boost personalization at scale.
3. Competitive advantage and market trends
Market dynamics analysis through BI tools reveals opportunities before competitors spot them. Companies can anticipate market changes, detect emerging trends, and quickly adapt their strategies. BI helps businesses understand customer segments first, enabling them to develop targeted marketing strategies that capture new opportunities. Companies with modern data systems gain a competitive edge by acting on real-time information.
4. Data-driven culture and governance
A data-driven culture treats data as a key resource to utilize insights across departments. Teams collaborate more effectively, gatekeepers are eliminated, and data access becomes more democratic. Of course, proper governance will provide you with data security, quality, and compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA. Companies that utilize BI strategically transform raw data into useful insights that drive breakthroughs.
Implementing a Business Intelligence System
Your BI implementation requires proper planning and careful execution to transform data into actionable business insights. A good BI system should be deployed with care to maximize your return on investment. To ensure smooth implementation, consider the following steps:
1. Lining up BI with business goals
Business alignment helps drive BI adoption. Your data strategy needs clear objectives that connect with measurable business outcomes. BI initiatives should push your organization toward its goals. Business and technical teams should meet regularly to promote productive discussions about specific data needs.
2. Choosing the right BI tools
The right BI platform seamlessly integrates with your existing data sources without requiring changes to your infrastructure. The tools should enable live data access without downloads and support your current data strategy. You should assess them based on enterprise reporting needs, embedded analytics capabilities, and how well they work with your data warehouse.
Moreover, consider your level of Enterprise Intelligence adoption. The platform you choose should be scalable to match your organization’s maturity and future growth in using data for strategic decisions.
3. Building a BI team and data strategy
Simply implementing BI tools isn’t enough to get the full value from your data. You need a dedicated team and a clear plan to turn raw data into a competitive advantage. A well-laid-out BI team has:
- BI analysts who turn complex data into useful insights
- Data architects who design practical frameworks
- BI developers who build technical tools and systems
Small projects can start with 2-3 analysts. You can add specialized roles like data scientists as your needs grow. The initial core team can focus on creating a solid foundation for your data strategy, ensuring your early projects deliver clear, measurable value to the business.
4. Overcoming data integration challenges
Data integration faces hurdles like inconsistent formats, API limitations, and legacy system silos. ETL tools help standardize data before it enters your BI system. You can utilize middleware solutions to manage API responses and ensure data flows smoothly.
5. Ensuring user adoption and training
BI adoption stays at 29% in most organizations, despite its benefits. The best approach is to provide training at the right time. Short sessions before launch work well when combined with detailed training after implementation. You should tailor training to different user roles and include company-specific examples to make it more relevant.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between OLAP and traditional databases?
OLAP (Online Analytical Processing) serves as a versatile tool that analyzes data in multidimensional databases. Users can isolate specific information pieces and examine them from multiple perspectives. OLAP stands apart from traditional databases by allowing simultaneous comparisons across different dimensions.
What are aggregate tables in BI?
Aggregate tables provide summaries of existing data warehouse information, typically displaying yearly or monthly metrics. Query times decrease significantly because these tables provide pre-calculated summaries, eliminating the need to retrieve millions of records.
How do dashboards function in business intelligence?
BI dashboards combine essential information into visual displays that show a business’s performance at specific points in time. The software’s user-friendly interface can be customized easily and pulls immediate data through business intelligence applications.
Achieve Organizational Success With Business Intelligence
Business intelligence serves as one of the core foundations of Enterprise Intelligence, transforming raw data into practical insights for strategic decisions. A strong BI strategy is crucial for businesses to stay competitive. Companies that properly use BI are more successful at getting customers, increasing profits, and running better operations.
Maximize Your Business Intelligence!
Transform your business intelligence into Enterprise Intelligence.
Learn More

Enterprise AI Search: Definition, Benefits, and Evolution

The Benefit of Company-Wide Knowledge Management in 2026

Are You Making These Common Knowledge Sharing Mistakes?
Estimate the Value of Your Knowledge Assets
Use this calculator to see how enterprise intelligence can impact your bottom line. Choose areas of focus, and see tailored calculations that will give you a tangible ROI.

Take a self guided Tour
See Bloomfire in action across several potential configurations. Imagine the potential of your team when they stop searching and start finding critical knowledge.