How to Set Up a Knowledge Management System

Summary
- The eight steps to set up a knowledge management system involve designing governance, selecting the right platform, developing a content structure, piloting, training users, incentivizing contributions, establishing metrics, and planning for content maintenance.
A KM must have these core elements: user-friendliness, robust search, appropriate technology, strong security, and a supportive knowledge-sharing culture.
Common challenges that undermine KMS success include a lack of employee awareness, insufficient time, and a culture that discourages sharing. Exacerbated by knowledge hoarding, information decay, and findability issues, they can lead to corporate amnesia and resistance to the adoption of new technology.
Setting up an effective knowledge management system (KMS) is a strategic project that goes beyond simply installing software. It fundamentally involves standardizing how your organization captures, shares, and uses its collective expertise. The process begins with clearly defining your business objectives and auditing the existing knowledge to identify critical gaps and key subject matter experts.
A successful KMS implementation focuses as much on fostering a knowledge-sharing culture as it does on selecting the right technology to set up a knowledge management system, ensuring high user adoption and sustained value.
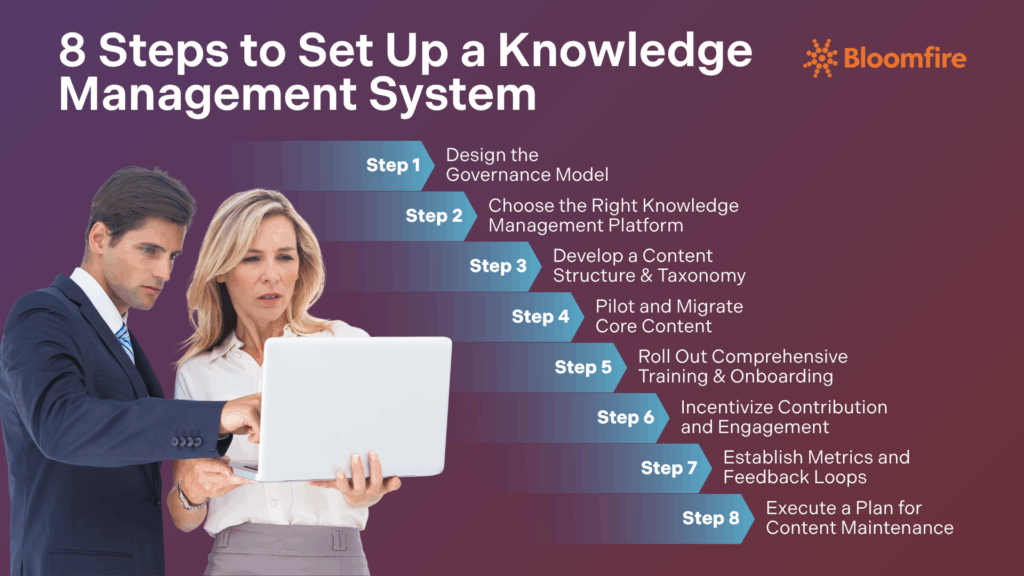
Step 1: Design the Governance Model
Your knowledge management needs strong governance as its foundation. A good governance model defines information ownership and decision-making processes, ensuring that your knowledge remains accurate and accessible over time.
Good governance is essential when establishing a knowledge management system. This is because the first step in developing a knowledge management system is to ensure a strong framework that prevents your knowledge base from becoming cluttered with outdated or incorrect information, which can be costly to rectify. It provides a reliable way to deliver the right information to the right people at the right time.
A complete governance model has three main layers:
- Strategic layer: Executive stakeholders who set goals, provide resources, and arrange knowledge management with the business strategy
- Operational layer: Knowledge managers and subject matter experts who handle daily tasks like content reviews and updates
- Technology layer: Platforms and tools that create a reliable infrastructure to manage knowledge
Most companies establish a Knowledge Council—a team from various departments that meets frequently to guide strategy and coordinate governance for how to build a knowledge management system. This helps break down barriers between business units and prevents the formation of isolated knowledge pools..
These core roles need clear definitions to succeed in the introduction of knowledge management:
- Knowledge manager: The vital role that drives knowledge management success and sets vision and strategy
- Content creators/knowledge workers: Handle knowledge throughout the content lifecycle
- Subject matter experts (SMEs): Check information accuracy without changing the structure
- Approvers/owners: Make final decisions on published content
Governance needs constant attention throughout the knowledge management system implementation lifecycle. Regular reviews help your knowledge management system stay effective as your organization grows and changes.
Step 2: Choose the Right Knowledge Management Platform
Your knowledge strategy needs a solid foundation: the right knowledge management platform. Start by assessing your organization’s specific needs and pain points. Think over whether you need a solution that handles internal documentation, customer support, or sales enablement.
The next step involves identifying features that match your requirements. User-friendly interfaces should be your top priority, as poor usability reduces adoption rates and wastes your investment. A reliable search capability becomes vital here–it saves up to 35% of time when looking for information.
AI-driven features deserve your attention because they boost efficiency by 40% through automated categorization and individual-specific recommendations. The platform should seamlessly integrate with your existing software ecosystem, which improves collaboration by 30% and eliminates information silos.
Data protection and regulatory compliance features protect your sensitive information. Cloud-based, expandable solutions work best for growing organizations that need to adapt to an expanding workforce.
Take advantage of free trials or demos to test different solutions. Your potential power users should provide feedback. Software review websites help you compare ratings and features based on your assessment factors.
Note that the platform with the most features may not be your best option when setting up a knowledge management system. Success depends more on adoption and integration than capabilities alone.
Step 3: Develop a Content Structure & Taxonomy
Your next vital step after picking a platform is to set up your content. A well-structured taxonomy serves as the GPS for your organization’s knowledge, guiding users quickly from broad topics to specific answers.
A logical content hierarchy saves time by a lot—employees waste 1.8 hours daily (9.3 hours weekly) looking for information. So you need to build a logical content hierarchy within your company’s knowledge management system.
Start by creating clear categories that match how users search, rather than following internal structures. The best taxonomies are broad and shallow rather than narrow and deep. Research shows success rates drop sharply beyond three levels of hierarchy (89% at 1-2 levels versus just 31% at 5+ levels).
As you design your structure:
- Build mutually exclusive, collectively exhaustive categories with clear labels
- Use consistent tagging and metadata to make content easier to find
- Create with your audience in mind and use familiar language
- Limit top-level categories to 5-9 items to help manage cognitive load
Remember that each piece of content should address only one problem. This makes information easy to follow. The structure should also reflect your organization’s workflow, not just how files are currently arranged.
Your taxonomy requires regular updates to stay current with changing terminology, technology, and user needs, which is a crucial aspect of managing knowledge effectively. This ensures it remains relevant and continues to work well over time.
Step 4: Pilot and Migrate Core Content
Your knowledge management system should be tested through a pilot project after establishing the taxonomy. A pilot project helps you verify your approach in a controlled setting before implementing it across the organization.
The first step is to pick a strategic pilot area that aligns with your organization’s objectives. You should select a department or team that can produce measurable, positive outcomes and scale well for future growth. This pilot serves as your testing ground to refine the knowledge management model and foster knowledge management behaviors.
The pilot phase requires a complete content inventory that sorts existing information by quality and relevance. Your team should map this content to the new structure and taxonomy for an uninterrupted transition. The next step involves converting content into compatible formats while keeping essential metadata such as tags and keywords.
The pilot’s feedback helps you assess system performance and tackle any issues. This valuable input serves as the foundation for improving your approach before wider implementation.
Content migration requires careful planning that extends beyond simply moving files. Your team should track existing resources, eliminate duplicates, and protect sensitive data throughout the process. The system’s primary goal is to create a well-organized repository where staff members can quickly find the necessary information without encountering outdated content.
Step 5: Roll Out Comprehensive Training & Onboarding
Training is the lifeblood of successful knowledge management system adoption. Companies spend about USD 954 per learner annually to develop their employees. Despite this, 58% of businesses still use paper-based, convoluted onboarding processes. This creates unnecessary friction for new hires.
Organizations that optimize their onboarding procedures see amazing results. Employee productivity jumps by 70% and retention rates improve by 82%. Your new employees should start using your knowledge platform right from day one to boost their productivity.
The most effective way to make an impact is to create customized training programs tailored to specific roles and technical expertise levels. Different learning styles need different approaches. You can utilize video tutorials, interactive modules, and quick-reference guides. Hands-on workshops provide users with practical experience in using system features.
Your training approach should make knowledge management a natural part of daily work. User guides and support resources enable employees to solve problems independently. Mobile accessibility becomes crucial because employees need information at any time and from any place.
Good training turns your knowledge management system from a simple storage space into a powerful collaboration platform. This leads to faster adoption and value creation across your organization. You’ll build strong foundations for continuous learning and improvement.
Step 6: Incentivize Contribution and Engagement
Knowledge management system adoption thrives on strategic incentives. Knowledge sharing rarely fits into standard KPIs, unlike most workplace tasks. This creates a need for planned motivation to sustain participation.
Gamification emerges as an effective solution. Organizations create enjoyable, competitive environments by introducing points, badges, and leaderboards that enhance engagement. Companies that combine gamification with knowledge-sharing technology see a remarkable 45% increase in employee engagement. This is a significant development, as it indicates that systems incorporating gaming elements perform more effectively.
Simple pointification won’t work–just adding gaming elements without linking them to company goals. The most effective incentive systems directly link knowledge contributions to business objectives. Points should be awarded to employees who share insights, respond to discussions, or create high-quality documentation.
Recognition motivates people without spending money. Here’s what works:
- Team meeting shoutouts
- “Knowledge sharer of the month” awards
- Digital badges for peer recognition
- One-on-one top contributor appreciation
The most effective results are achieved by combining individual and team incentives. While experts debate the effectiveness of incentives, studies confirm that recognition fosters positive behaviors. This creates an environment where knowledge flows naturally across your organization. Your knowledge management system evolves from a static database into a vibrant hub of shared expertise.
Step 7: Establish Metrics and Feedback Loops
Success measurement plays a crucial role in the implementation of knowledge management systems. Your KMS needs proper metrics to determine its value and identify areas that need adjustment.
A clear monitoring plan should address key questions:
- What do you want to achieve?
- Which resources need monitoring?
- How frequently should you check these resources?
- What tools will help? Who takes charge of monitoring?
- Who gets notified about problems?
You need baseline metrics in four key areas to measure effectiveness:
- Activity metrics: Monitor participation through system logins, knowledge contributions, and document views. Note that login counts alone don’t show how well the system works.
- Satisfaction metrics: Users should provide direct feedback about the platform’s usefulness, interface quality, and content relevance.
- Business impact metrics: Link KM activities to real results like lower project costs, faster cycle times, or better innovation. These metrics appeal to leadership teams.
- Capability metrics: Assessing the maturity of your KM program through established frameworks. You can even push it higher by understanding your Enterprise Intelligence maturity.
The platform should include feedback mechanisms that create improvement loops. Quick responses to user suggestions and regular update communications help. This strategy helps your KMS evolve from a static repository into a dynamic system that meets organizational needs.
Step 8: Execute a Plan for Content Maintenance
A systematic approach to content maintenance determines the longevity of your KMS. The best KMS can quickly become a collection of outdated information without regular updates, which can be costly and result in missed opportunities.
Your knowledge base needs someone clearly responsible for it. Select someone within your company to oversee the ongoing management strategy and ensure content is updated regularly. This person should oversee information quality, remove outdated content, and add new features as needed.
Here’s what you need to do to maintain your system:
- Schedule periodic knowledge audits to verify the accuracy and quality of your resources, and review the content to ensure it is up-to-date.
- Track usage analytics to identify knowledge gaps, failed searches, and assess content performance.
- Set up feedback channels with embedded forms, ratings, or simple thumbs-up/down options so users can easily flag any issues.
- Sort feedback by urgency and importance, then act quickly on what users suggest.
- Align update processes with other company activities—update customer-facing content immediately after refreshing product training materials.
Companies should assess their knowledge management strategies at least every two years, although more frequent reviews are also effective. Your maintenance plan should create a system that evolves with your organization, rather than becoming outdated.
Key Considerations When Developing a Knowledge Management System
Developing an effective KM system requires attention to several factors that transcend simple implementation steps. Lacking clear knowledge goals and objectives means even the most advanced KM tool will fail to deliver meaningful value, as the system must be directly aligned with established business goals.
These fundamental elements and features help transform a knowledge management system from a simple storage space into a powerful, strategic asset.
- User-friendliness: This stands as the top priority; users will quickly abandon complex interfaces, ultimately wasting your investment and killing user adoption.
- Robust search functionality: Your system needs solid search capabilities to prevent frustrating “it was supposed to be here” moments, which are a major factor in user disengagement.
- Technology selection: Organizations often mistakenly believe one technology can manage all knowledge tasks; however, combining multiple specialized solutions frequently yields better results tailored to specific organizational needs.
- Security and compliance: Security practices require careful attention, including implementing encryption, adhering to regulations such as GDPR, and enforcing role-based access controls. This ensures sensitive data remains confidential while authorized team members maintain easy access.
- Cultural fit: Research shows that cultural factors significantly affect system effectiveness, necessitating that companies actively foster an environment where knowledge sharing becomes a natural part of daily work. This culture can be fostered through structured mentorship programs and the formal recognition of employees who make valuable contributions.
Leaders must commit to continuously refining these factors, ensuring the system remains relevant, secure, and fully adopted by the workforce. Adhering to these principles ensures the KM system becomes a central tool for achieving strategic business outcomes. This commitment to structure and usability ensures your intellectual capital is readily accessible and actively used by all employees.
Common Challenges in Setting Up a Knowledge Management System
Research indicates that awareness, time, and culture are the primary factors that contribute to the failure of knowledge management efforts. Employees often lack awareness of available tools. They can’t find time for knowledge activities. The workplace culture doesn’t encourage sharing. Companies don’t deal very well with:
- Knowledge hoarding: Employees hold back their expertise because they fear losing their unique value or worry about job security
- Information and data decay: Knowledge bases quickly fill with irrelevant or obsolete data without regular updates
- Findability issues: Poor organization and weak search features waste about 1.8 hours each day as employees search for information
- Corporate amnesia: Companies lose ground when the core team leaves, and many see damaged client relationships
Technology adoption adds another layer of complexity when you set up a knowledge management system. About 70% of change programs fail because employees resist them. This pushback typically occurs because employees feel overwhelmed by the constant changes in tools.
A Steady Stream of Enterprise Intelligence with KMS
Modern knowledge management systems are more than mere repositories; they actively transform raw institutional knowledge into Enterprise Intelligence, providing leaders with unparalleled operational clarity. It ensures that valuable expertise is analyzed, distributed, and applied across the organization, creating a continuous feedback loop of informed decision-making.
So choose a KMS that secures a competitive advantage, making the collective wisdom of your organization a powerful, accessible, and dynamic asset for driving future success.
Get Enterprise Intelligence
Bloomfire converts your expertise into strategic, measurable business value.
Consult our Expert
Start by identifying specific knowledge needs and arranging them with your organizational goals. A successful implementation needs clear processes to capture, organize, and share knowledge across departments. Strategy and planning should precede implementation. Your technology choice should support defined processes, rather than forcing processes to fit the technology.
A well-configured KMS creates a central repository where employees can access information at any time, promoting a collaborative work environment. Companies with strong knowledge management programs see a 10% boost in cross-functional collaboration. Teams can use collective experiences to solve challenges more effectively and avoid redundancy. Collaboration platforms with discussion boards and Q&A features also promote interactive communication. Knowledge sharing enables diverse teams to bring fresh perspectives to solve complex problems more effectively.
Companies often rush into knowledge initiatives without proper planning or strategy. One major mistake is treating the knowledge base as a one-time project rather than an ongoing process. Another error involves creating overly complex systems—users revert to asking colleagues directly when they need multiple clicks to find simple information.
Set clear objectives that match your company’s business goals. The program is more successful when you solicit input from employees at all levels. Define knowledge management processes with detailed procedures before choosing technology. Use a phased approach, starting with a pilot project to test and refine before full deployment. Choose technology that meets security and compliance requirements after consulting with IT. Build a knowledge-sharing culture by recognizing contributions and showing benefits to employees.
A good KMS delivers measurable improvements, including increased team efficiency and enhanced customer retention. Teams spend less time searching for information, which substantially boosts productivity. Organizations make better decisions by having access to accurate and current information. Customer service teams can give consistent responses that build customer trust. Other benefits include faster onboarding, lower training costs, and the preservation of institutional knowledge despite employee turnover.
Bloomfire’s Ignition Sequence connects you with dedicated experts in knowledge management and change management to help you reach your adoption goals. The platform utilizes AI-powered search and discovery tools that provide relevant answers quickly, saving time previously spent on ineffective filing systems. Its flexible building blocks help tailor your

How to Improve Customer Service: 9 Strategies to Automate Success

7 Best Customer Service Knowledge Management Systems in 2026

The 6 Knowledge Management Trends That Redefine Strategic Intelligence in 2026
Estimate the Value of Your Knowledge Assets
Use this calculator to see how enterprise intelligence can impact your bottom line. Choose areas of focus, and see tailored calculations that will give you a tangible ROI.

Take a self guided Tour
See Bloomfire in action across several potential configurations. Imagine the potential of your team when they stop searching and start finding critical knowledge.