The Knowledge Management Process: A Roadmap to a Successful Implementation Program

Navigating the intricate world of knowledge management is more than a strategic initiative; it’s about connecting people with the information they need at the right time. As someone who’s helped launch successful knowledge management programs for various organizations, I’ve seen firsthand how the right approach can transform business processes. It’s not just about managing information; it’s about fostering a culture where knowledge sharing becomes second nature.
In this guide, we’re going deep into the knowledge management process. Learn the essential steps and strategies that make up an achievable knowledge management roadmap, all through the lens of practical, real-world application.
What Is a Knowledge Management Process?
A knowledge management process is a structured approach organizations use to identify, create, store, share, and utilize the collective knowledge and information within the organization. Its primary goal is to make the right knowledge available to the right people at the right time to improve decision-making, enhance efficiency, foster innovation, and retain valuable expertise.
A robust knowledge management process flow transforms raw data and individual insights into accessible and actionable organizational assets. As a result, critical information or data doesn’t reside in silos or walk out the door when employees leave.
While often used interchangeably, the knowledge management cycle typically refers to the iterative nature of the knowledge management process. New knowledge is constantly being generated, captured, and integrated back into the system, perpetuating the cycle and continuously enriching the organization’s collective intelligence.
Initial Steps: Laying the Foundation for Knowledge Management
The journey to effective knowledge management begins with a solid foundation. This critical first step involves a comprehensive audit of your organization’s current state of knowledge, understanding what information you have, where it resides, and how it is accessed and used.
A crucial part of this process is identifying your business’s specific knowledge needs and the gaps in your current knowledge management system. It’s about pinpointing where your knowledge assets fall short and creating a plan to bridge these gaps.
To gain a holistic view, you should involve various organizational stakeholders in this initial phase. This collaborative approach ensures that your knowledge management strategy is inclusive and aligns with your organization’s diverse needs and functions.
Whether streamlining decision-making, enhancing employee collaboration, or improving customer service, understanding these goals is paramount. With this insight, you can begin to chart a course for a knowledge management process that addresses your immediate needs and positions your organization for future growth and adaptability.
Streamline Your Knowledge Management Process
Leverage Bloomfire’s wealth of KM tools to implement an effective KM process.
Explore Bloomfire
Assessing and Identifying Existing Knowledge
Internal knowledge assessment involves engaging with employees at all levels to understand their daily information needs and identifying subject matter experts. It also encompasses analyzing workflows to see where knowledge is created and used, and reviewing existing documents and data repositories. Here are some tips for assessing and identifying knowledge:
- Analyze existing documents, reports, and data to extract valuable insights and knowledge.
- Look for recurring questions or issues that indicate a lack of accessible knowledge.
- Inventory existing knowledge repositories and assess their effectiveness and content.
Conducting this thorough evaluation is crucial to establishing a knowledge management life cycle that effectively meets the organization’s needs and drives successful outcomes. Prioritize knowledge needs based on their potential impact on efficiency, innovation, and decision-making.
Uncovering Knowledge Gaps
Many organizations face knowledge gaps, with a striking 87% reporting current or anticipated skills shortages, according to McKinsey & Company. This is why identifying where critical knowledge is missing or difficult to access is vital to establishing an effective knowledge management process.
In doing so, you must look beyond existing documented knowledge to understand what employees struggle to find, where bottlenecks occur due to a lack of information, and what expertise walks out the door when someone leaves. Here are some ways to uncover knowledge gaps:
- Conduct post-project reviews and retrospectives to identify what knowledge was missing or could have improved outcomes.
- Perform skills inventories and competency mapping to identify areas where critical expertise is lacking or concentrated in only a few individuals.
- Solicit feedback from employees through surveys, interviews, or focus groups about information they need but cannot easily find.
- Review training materials and onboarding processes to see where new employees consistently struggle due to missing information.
Pinpointing knowledge gaps enables organizations to focus on acquiring, creating, and disseminating the information necessary to enhance operations, resolve problems, and drive innovation. Once these gaps are identified and your existing knowledge assessed, you’ll have a clearer direction toward structuring your knowledge management process.
The 9 Stages of the Knowledge Management Process
Embarking on the knowledge management journey involves several key stages. Each stage represents a critical step in building a robust and effective knowledge management process. This consists of implementing tools and creating a holistic approach that aligns with your organization’s objectives and culture.
In the following sections, we’ll break down these stages, offering insights into how each contributes to the overall success of your knowledge management roadmap efforts.

Stage 1: Evaluating Current Knowledge Infrastructure
The first stage for optimizing your knowledge management process involves thoroughly evaluating your existing knowledge infrastructure. This step is crucial as it lays the essential groundwork for a successful knowledge management strategy. It incorporates several key elements:
- Assessment of current systems: Scrutinize your current knowledge landscape. Examine precisely how knowledge is currently stored, the methods employed for sharing information across the organization, and the ease or difficulty team members face accessing needed insights. Consider the technologies in place and the informal channels utilized.
- Identification of strengths and weaknesses: Identify what works well within your existing systems and knowledge management practices. Equally important is revealing the current limitations, inefficiencies, knowledge gaps, and potential redundancies. This involves evaluating effectiveness, accessibility, and the overall flow of organizational knowledge.
- Informing strategy development: Leverage the insights gathered from assessing systems and identifying strengths and weaknesses. This crucial information will directly shape and guide the development of a robust and effective knowledge management strategy tailored to your organization’s specific needs and realities.
This first step of the KM process ensures all subsequent actions build upon a clear picture of your knowledge ecosystem, leading to more targeted and effective improvements. Consequently, resources and efforts are focused precisely where they will yield the greatest positive impact on your knowledge operations.
Stage 2: Defining Knowledge Management Goals and Leadership
Transitioning from the evaluation phase, stage two centers on defining clear, actionable knowledge management goals and identifying the appropriate leaders and stakeholders vital for your KM initiative’s success. This crucial phase incorporates several critical steps:
a. Establishing Measurable Goals
Clearly articulate specific, quantifiable goals for your knowledge management endeavors. Define precise targets that allow for tangible measurement of progress and impact.
For example, objectives should be established, such as reducing the average time required to onboard new personnel, improving customer satisfaction metrics (CSAT scores), or achieving verifiable gains in operational efficiency across teams. The emphasis here is on setting targets you can track and validate.
b. Exploring a Spectrum of Objectives
Consider a wide array of potential objectives that knowledge management can influence. Think expansively about areas KM can support. These could be elevating internal communication flows or boosting employee engagement levels. They might also significantly enhance customer satisfaction outcomes, foster a more innovative organizational culture, or address any specific area connecting directly with your organization’s strategic priorities and operational needs.
c. Ensuring Strategic Cohesion
The goals you establish must be measurable and align seamlessly with your overarching organizational objectives. This coherence ensures that your knowledge management work directly supports and contributes to your company’s broader success and strategic direction. The aim is to make KM an engine for achieving business outcomes.
d. Identifying and Engaging Key KM Leaders and Stakeholders
Actively engage the essential individuals who will champion, guide, and support your knowledge management initiatives from various organizational levels. This critical group may encompass dedicated KM program managers, content experts, curators responsible for ensuring knowledge quality, and technology specialists overseeing the platforms. It also includes departmental representatives who ensure KM meets the team’s diverse needs.
Defining precise and measurable knowledge management goals and selecting a dedicated team to champion these efforts provides a sharp focus for all subsequent KM activities. This establishes a robust foundation essential for the successful implementation and ongoing evolution of your knowledge management strategy.
Stage 3: Developing Your Knowledge Management Strategy
In stage three, the central effort shifts to crafting a robust, comprehensive knowledge management strategy. This pivotal phase outlines precisely how your organization will harness its collective intelligence. Essential elements incorporated within this stage include:
- Blueprint creation: Develop a detailed blueprint that clearly defines the processes, technologies, and responsibilities required for capturing, meticulously managing, and effectively disseminating knowledge throughout the organization. Design workflows for knowledge flow, select appropriate tools, and assign ownership for different aspects of the strategy.
- Addressing challenges and opportunities: Directly integrate the valuable insights harvested from earlier assessments, along with the identified strengths, weaknesses, challenges, and emerging opportunities. Tailor the strategy’s design to proactively address unique organizational needs and capitalize on areas ripe for enhanced knowledge leverage.
- Integration into operations: Plan for the seamless embedding of knowledge management within the fabric of your business culture. This involves identifying how knowledge access and sharing become intuitive parts of workflows, exploring the necessary training, and fostering a cultural environment that encourages contribution and seeking knowledge.
A meticulously developed strategy stands as a cornerstone for your knowledge management program’s successful integration and overall effectiveness. It provides the essential roadmap, ensuring efforts align with strategic goals and deliver tangible value.
Stage 4: Selecting the Right Knowledge Management Tool
Selecting the appropriate KM technology is pivotal in establishing an effective knowledge management system. This decision holds significant weight and requires a thorough evaluation of various software options. The assessment should center on core aspects such as each tool’s capabilities, ability to grow with your organization, and compatibility with your existing technical environment.
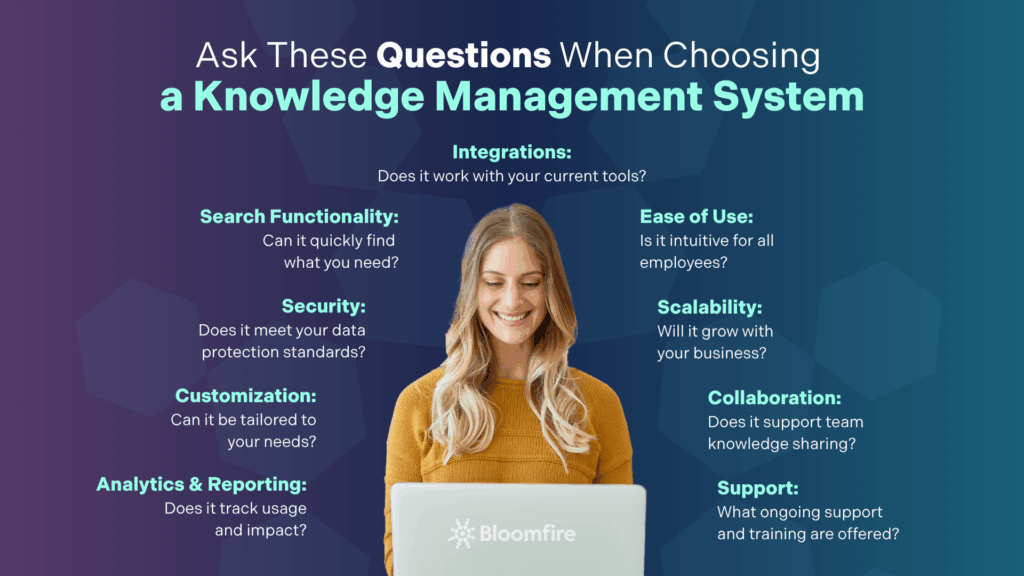
Identifying the ideal tool necessitates careful consideration of specific qualifications and posing key questions during the evaluation process. Here’s a list of key qualifications and questions to consider when evaluating potential tools:
- Integration capabilities: Does the tool integrate seamlessly with your existing systems and workflows?
- User-friendliness: Is the interface intuitive and easy for all employees?
- Scalability: Can the tool grow and adapt as your organization evolves?
- Collaboration features: Does it facilitate effective collaboration and knowledge sharing among teams?
- Search functionality: How robust are its search capabilities in retrieving relevant information quickly?
- Data security: Does the tool meet your organization’s security and privacy standards?
- Customization options: Can it fit your organization’s needs and structure?
- Analytics and reporting: Does it offer comprehensive analytics to track usage and the impact on knowledge management?
- Vendor support and training: What ongoing support and training does the vendor provide?
The right tools will enhance efficiency and ensure that knowledge flows smoothly across your organization. Considering KM platforms like Bloomfire, which offer powerful AI-powered search, facilitate dynamic Q&A, and build a connected knowledge community, can be particularly impactful. It empowers users to find trusted answers and connect with subject matter experts quickly, aligning perfectly to create a vibrant and accessible knowledge ecosystem.
Stage 5: Structuring Your Knowledge Management System
Structuring your system is one of the critical steps in knowledge management. This stage focuses on organizing and classifying knowledge logically, ensuring alignment with established principles for efficient knowledge management. Key components of this crucial phase include:
- Logical categorization: Establish clear, intuitive categories or defined topics. This segmentation is crucial for effectively grouping and organizing knowledge assets, making information easier to navigate and locate.
- Seamless accessibility: Ensure all relevant individuals can easily access the necessary knowledge. The system should remove barriers to access for authorized users, making necessary information readily available at their fingertips whenever and wherever they need it to perform their roles effectively.
- Proactive knowledge curation: Implement processes that ensure the content remains current, accurate, and valuable over time. Regular review, updates, and refinement of knowledge assets prevent information and data decay, maintaining the system’s credibility and usefulness as a reliable source.
- Intuitive user experience (UX) design: Develop an interface that is straightforward, easy to use, and pleasant to interact with. A well-designed user experience encourages people to engage with the system regularly, facilitating both the contribution and retrieval of knowledge.
This stage is about creating a system that stores knowledge and makes it a living, breathing part of your organizational ecosystem. It facilitates easy access to vital information and promotes frequent and valuable use across teams. If you already have a structure, don’t forget to perform regular knowledge management audits.
Stage 6: Implementing the Knowledge Management System
Stage six represents the critical phase where your knowledge management strategy transitions from planning into active operation. This is the point at which the chosen system and refined processes are implemented across your entire organization. The knowledge management implementation stage encompasses several vital activities:
- Training and Onboarding: Equip your team with the necessary skills and knowledge to utilize the new system effectively. This involves comprehensive education on how to contribute knowledge, search for information, and leverage the system’s features to enhance their daily work.
- Phased Rollout: Consider deploying the system incrementally across different departments or user groups. A phased approach enables testing, gathering initial feedback, and refining the process in a controlled environment before a full organizational rollout.
- Establishing a Feedback Mechanism: Create accessible channels for users to provide input on their experience with the new system. Collecting feedback is essential for identifying challenges, understanding user needs, and making necessary adjustments to continually improve usability and effectiveness.
Executing these steps diligently makes the system fully operational and functional. It ensures the deployed solution aligns well with user expectations and overarching business objectives.
Integrating Knowledge Management into Daily Operations
A key to better KM adoption and seamless change management is maximizing the use of the tool in your employees’ daily routines. When the knowledge management system is integrated into your organization’s daily operations, you can maximize its return on investment (ROI) and ensure your KM process is not treated as an afterthought. This integration often involves:
- Incorporating KM practices: Embed knowledge management activities into everyday work processes. For example, you can make document sharing and lessons learned capture a non-negotiable part of your project management workflows.
- Promoting a knowledge-sharing culture: Encourage and incentivize employees to actively contribute and use the system. Consider offering helpful rewards for helpful contributions.
- Linking KM to performance metrics: Connect knowledge management activities with key performance indicators to underline its value. For instance, measure how accessible documentation of common issues correlates with a reduction in average customer support resolution times.
This integration ensures that knowledge management becomes an integral part of the workflow rather than an isolated function. The effectiveness of such integration is echoed in the experience of Dexcom.
Stage 7: Embedding Knowledge Management in Operations
Stage seven focuses on deeply embedding knowledge management so it becomes an intrinsic, seamless component of your organizational operations and culture. This phase moves KM beyond a standalone initiative, integrating it into the daily rhythm of work. Achieving this level of integration involves several key endeavors:
- Operational alignment: Ensure the knowledge management system and its associated practices align with your core operational processes and overall business strategies. This means integrating KM workflows directly into how tasks are performed, decisions are made, and projects are executed, making it a natural part of work rather than an add-on.
- Long-term integration: Develop proactive strategies to sustain and strengthen knowledge management’s role within daily operations over the extended term. This includes planning for system maintenance, ensuring content freshness, facilitating process evolution, and cultivating a workplace culture that values sharing and learning as ongoing activities.
- Continual reinforcement: Regularly highlight and reinforce the importance of active knowledge management practices throughout the organization. This can involve consistent messaging from leadership, ongoing opportunities for skill development related to the system and KM principles, and recognition programs that celebrate contributions to the shared knowledge base. This helps solidify KM as a valued behavior.
While embedding KM into operations, organizations often encounter challenges such as securing employee and leadership buy-in, managing technology fatigue, handling information overload, documenting knowledge effectively, and ensuring content trustworthiness. Navigating these challenges is crucial for KM to become a natural and essential part of the organizational ecosystem, continually driving value and improvement.
Stage 8: Managing and Enhancing the Knowledge Management System
This stage involves the ongoing management and enhancement of the system, which is crucial in the knowledge management process for maintaining the system’s relevance and effectiveness. This includes:
- Regular Reviews: Establish a schedule for periodic system evaluations. This can involve collecting user feedback through surveys, monitoring usage statistics, and meeting with key stakeholders to discuss system performance and user satisfaction. The goal is to identify areas for improvement and ensure the system meets current organizational needs.
- Updating Content: Develop a routine for reviewing and updating content. Assign responsibility to specific team members or departments for regularly checking the accuracy and relevance of information in their areas of expertise. Implement a system for flagging outdated or irrelevant content for review or removal, and encourage continuous contributions of new and updated information.
- Technological Upgrades: Outdated systems can hinder collaboration, slow down access to critical information, and fail to support new knowledge formats or analytical capabilities, ultimately leading to stagnation and decreased effectiveness of KM efforts. Organizations should assess their current KM framework to implement technological upgrades effectively and identify pain points or limitations.
Effectively managing these aspects is crucial to ensure your knowledge management system remains a dynamic and valuable resource. It is essential to remember that a knowledge management system is only as good as the knowledge it contains, so adapting to changing organizational needs and ensuring that the content is regularly updated and relevant is critical to maintaining its effectiveness and value.
Monitoring, Evaluating, and Adapting Knowledge Management Practices
An essential part of managing your knowledge management system involves monitoring its usage and efficacy, evaluating its impact on business outcomes, and adapting based on the insights gathered. Regularly tracking performance helps identify how effectively the system is being utilized.
Concurrently, actively seeking user feedback can uncover areas needing improvement or enhancement. Adaptability in making changes ensures that the knowledge management system evolves to meet your organization’s and its users’ dynamic needs.
In addition to these practices, defining and monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics that align with your organization’s goals is crucial. A sound KM system should include built-in analytics features, enabling you to track engagement and measure the impact of knowledge management on business outcomes. Effective analytics tools provide insights into user behavior, content effectiveness, and areas for improvement, guiding strategic decisions and continual refinement of KM practices.
Stage 9: Iterative Improvement and Adaptation
Iterative improvement and adaptation represent the critical and ongoing phase in the knowledge management roadmap, focusing intently on your knowledge system’s continuous evolution and refinement. This sustained effort involves several key practices:
- Continuous learning: Actively gain insights from user interactions, system performance metrics, and feedback mechanisms. Analyze usage patterns, identify content gaps, and learn from successes and challenges encountered during system use. This ongoing learning process directly fuels system enhancements.
- Cultivating flexibility: Maintain agility to respond effectively to emerging challenges, seize new opportunities, and integrate technological advancements. A flexible approach ensures the knowledge management system can pivot as business priorities change or as new ways of working emerge.
- Embracing an evolutionary approach: View knowledge management not as a fixed endpoint, but as a dynamic, living process designed to grow and mature alongside your organization. This perspective encourages ongoing investment and attention, treating the knowledge ecosystem as a strategic asset that requires continuous nurturing.
Focusing on this final stage ensures your knowledge management system remains perpetually relevant, highly effective, and capable of adapting seamlessly to your organization’s evolving needs and landscape. This commitment to ongoing refinement builds a resilient knowledge environment that continuously delivers value over the long term.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is a knowledge management process important for organizations?
A knowledge management process is vital because it prevents the loss of valuable organizational expertise and avoids the costly reinvention of internally developed solutions. It significantly improves decision-making speed and quality, enabling teams to access and leverage collective insights for faster, more effective problem-solving and enhanced innovation.
What are the biggest challenges in implementing a knowledge management process?
Implementing a knowledge management process often faces significant challenges rooted in organizational culture, particularly fostering a willingness among employees to actively share and reuse information. Technical hurdles also arise in selecting, integrating, and maintaining suitable platforms while managing the volume and ensuring the relevance of knowledge content. Furthermore, clearly demonstrating the measurable value and ROI of KM initiatives to secure sustained leadership support and necessary resources proves consistently difficult.
How does a KM process help a company improve continuously?
A knowledge management process helps a company improve continuously through the systematic capture and widespread sharing of valuable lessons learned and effective practices across the organization. Access to this shared organizational knowledge empowers employees to optimize workflows, enhance decision-making, and avoid recurring mistakes. Regular evaluation built into the process, often supported with user feedback and analytics, facilitates ongoing refinement of the knowledge base and the process.
Sealing the Knowledge Management Journey
A sustainable knowledge management process constitutes an ongoing journey of continuous improvement and adaptation, intrinsically linked to your organization’s evolution. The implementation stages provide a valuable roadmap, yet the true power resides in the iterative process of learning, refining, and growing the system over time. Embracing this dynamic approach transforms knowledge management into an invaluable strategic asset, significantly contributing to sustained success and fostering innovation.
Elevate Your Knowledge Management Strategy
Learn essential insights for building an effective KM process from our Value of Enterprise Intelligence Report.
Get the report

10 Best Knowledge Management Practices in 2026

Different Types of Knowledge: Implicit, Tacit, and Explicit

Striking the Right Balance Between AI and Human Customer Service
Estimate the Value of Your Knowledge Assets
Use this calculator to see how enterprise intelligence can impact your bottom line. Choose areas of focus, and see tailored calculations that will give you a tangible ROI.

Take a self guided Tour
See Bloomfire in action across several potential configurations. Imagine the potential of your team when they stop searching and start finding critical knowledge.