How to Organize a Knowledge Base: A Step-by-Step Guide

A robust knowledge base helps you unlock the full potential of your organizational knowledge, facilitating better decision-making and collaboration. Efficiently managing and organizing this knowledge can greatly enhance your organization’s productivity and innovation. This is also where knowledge management comes into play, providing the frameworks and strategies to transform raw data into actionable insights.
In this comprehensive guide, we will cover the steps to organizing your knowledge base, from setting your goals to choosing the right platform and structuring your content. We will also explore best practices, common pitfalls, and strategies for continuously improving your knowledge management system.
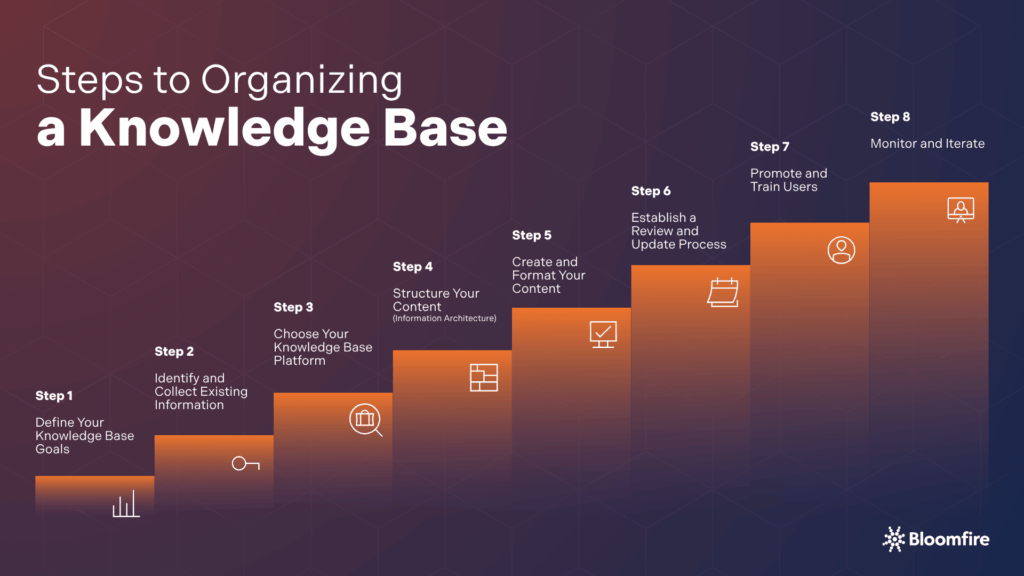
Step 1: Define Your Knowledge Base Goals
Identifying your specific goals and objectives marks the first step to answering the question of “how to organize a knowledge base.” Without a clear understanding of what you aim to achieve, your efforts to organize your knowledge base may lack direction and impact. 37% of projects, including knowledge base implementations, fail due to unclear project objectives and milestones.
Start by identifying the primary objectives of your knowledge base. Are you looking to improve customer support, streamline internal communication, or enhance training programs?
Once you have established your primary objectives, consider the specific outcomes you wish to achieve. For instance, if your goal is to enhance customer support, you might aim to reduce response times or increase the rate of first-contact resolutions. If your focus is internal, aim to facilitate cross-departmental collaboration or improve onboarding processes. Defining these specific outcomes will provide a clear roadmap for developing your knowledge base.
It is also essential to align your knowledge management goals with your organization’s overall strategic objectives. This ensures that your efforts in knowledge management contribute directly to your broader business goals. Regularly revisit and refine your goals to ensure they remain relevant and aligned with your organization’s evolving needs.
Step 2: Identify and Collect Existing Information
With your goals clearly defined, the crucial next step involves identifying and gathering your organization’s existing information. This means performing a comprehensive audit of your current knowledge assets. Understanding what information is already available will help you prevent duplication of effort and ensure your knowledge base is both thorough and up-to-date.
Here’s how to approach this process:
- Categorize information: Begin by classifying the various types of information your organization utilizes and generates. This could encompass product manuals, troubleshooting guides, FAQs, and standard operating procedures.
- Gather resources: Once categories are set, collect all pertinent documents and data. This may require coordinating with different departments or teams to access their files and resources.
- Assess relevance and accuracy: As you collect information, evaluate its relevance and accuracy. Obsolete or incorrect information can compromise your knowledge base’s effectiveness, so verify that all content is current and meets your organizational standards.
Taking these steps not only streamlines the development process for your knowledge base but also guarantees that it becomes a dependable resource for all users. Doing so allows for a more informed and efficient work environment.
Step 3: Choose Your Knowledge Base Platform
Choosing the ideal knowledge platform is crucial for the success of your knowledge base. The platform you select should align with your goals and support the types of content you plan to include. With numerous options available for building a knowledge base, ranging from open-source solutions to enterprise-level software, it’s essential to evaluate each one based on your specific needs.
When selecting a knowledge base platform, consider the following critical factors:
- Usability: The user experience should be intuitive, allowing users to find the information they need easily. This includes a clean interface, effective search functionality, and straightforward navigation.
- Scalability: The platform should be scalable and capable of accommodating future growth in both content volume and the number of users. This means it can handle increasing data and user loads without significant performance degradation.
- Integration capabilities: Look for seamless integration with existing systems, such as CRM (Customer Relationship Management) or help desk software. This enhances functionality, streamlines workflows, and avoids information silos.
- Security features: The platform must offer robust security features to protect sensitive information. This includes access controls, encryption, and compliance with relevant data privacy regulations.
- Search and retrieval: Beyond basic search, evaluate advanced search options, filtering capabilities, and how effectively users can retrieve specific information from an extensive knowledge base.
- Content creation and management: Consider the ease of creating, editing, organizing, and publishing knowledge base documents. Look for features like version control, content templates, and collaborative editing tools.
- Analytics and reporting: The platform should provide analytics and reporting features to track usage, identify popular content, and pinpoint knowledge gaps. This data is crucial for continuous improvement.
- Customization: The ability to tailor the platform’s appearance and functionality to align with your organization’s branding and specific needs is crucial for a personalized user experience.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including licensing fees, implementation costs, maintenance, and potential training expenses.
Solve Your Internal Knowledge Chaos
Get a powerful internal knowledge base that enhances employee access to critical information.
Schedule a Demo
To make an informed decision, involve key stakeholders in the selection process. This might include representatives from IT, customer support, and other departments that will frequently use the knowledge base. Their input can provide valuable insights into the features and functionalities that are most important for your organization. Once a platform is chosen, set it up in a way that aligns with your information architecture and organizational needs.
Step 4: Structure Your Content (Information Architecture)
Information architecture involves organizing content logically and intuitively, making it easy for users to navigate and find what they need. This step is critical in ensuring that your knowledge base is user-friendly and efficient.
A report by McKinsey found that employees spend, on average, 1.8 hours every day – or 9.3 hours per week–searching for information. This highlights the substantial time lost due to disorganized or hard-to-find internal resources.
Begin by defining a clear hierarchy for your content. This might involve grouping related topics into categories and subcategories. Use logical naming conventions and consider the user’s perspective when organizing content to ensure clarity and ease of use.
For a business organization, you might define a content hierarchy with a main category, such as “Employee Resources,” which could then have subcategories like “HR Policies,” “IT Support,” and “Training Materials.” Within the “HR Policies” section, you will find specific documents, such as “Leave Request Forms” and “Code of Conduct,” all organized logically for easy employee access.
Think about how users search for information and structure your content to match these patterns. A well-organized hierarchy simplifies navigation and enhances the overall user experience.
Step 5: Create and Format Your Content
Creating and formatting content is where the knowledge base truly comes to life. This step involves writing clear, concise, and accurate documentation that meets the needs of your users. High-quality content is essential for ensuring that your knowledge base is a valuable resource for your organization.
When creating content, such as articles for your knowledge base, focus on clarity and user comprehension. Here are the key steps to follow:
- Prioritize simple and direct language: Use straightforward vocabulary and sentence structures. Steer clear of jargon unless it’s essential and your target audience readily understands it.
- Break down complex information: Divide intricate topics into smaller, digestible sections. Use headings, bullet points, and numbered lists to significantly improve readability and allow users to scan for relevant information quickly.
- Incorporate visual aids: Enhance understanding and engagement by including images, diagrams, screenshots, and videos. Visuals can convey complex processes or concepts more effectively than text alone.
- Consider diverse formats and media: Don’t limit yourself to just text. Think about how multimedia elements can provide additional context and clarity. For instance, a written troubleshooting guide could be significantly enhanced by a short video demonstration of the steps.
- Maintain consistency: Ensure a consistent tone, style, and terminology throughout your content to maintain a cohesive narrative. This helps build a coherent and professional knowledge base.
- Focus on the user’s needs: Always write with your audience in mind. What questions are they trying to answer? What problems are they trying to solve? Tailor your content to directly address these needs.
- Include calls to action (where applicable): If the content requires a user to act, clearly state what that action is. This could be “Contact Support,” “Download this form,” or “Click here for more information.”
- Regularly review and update: Knowledge is constantly evolving. Schedule regular reviews of your content to ensure it remains accurate, relevant, and up-to-date.
To streamline the content creation process, assign roles and responsibilities to team members.
Our Value of Enterprise Intelligence Report shows that on average, companies typically have only one content contributor for every seven employees who access a knowledge management system. This ratio highlights a significant imbalance, underscoring the potential for a small group to bear a substantial burden in maintaining current and comprehensive information.
Encourage collaboration and peer reviews to ensure accuracy and comprehensiveness of the content. Remember, your knowledge base is a living document that should evolve with your organization.
Step 6: Establish a Review and Update Process
Develop a schedule for regular content reviews. This might involve quarterly audits or more frequent checks for high-priority information. Assign responsibility for content review to specific individuals or teams, ensuring accountability and consistency throughout the process.
During reviews, verify the accuracy of information, update outdated content, and remove any redundant or irrelevant material. In addition to scheduled reviews, establish a process for ad-hoc updates. This may involve a system for reporting inaccuracies or a protocol for incorporating user feedback.
Step 7: Promote and Train Users
A knowledge base is only effective if users know how to access and utilize it. Promote your knowledge base through internal communications, highlighting its benefits and available resources.
Consider offering training sessions or workshops to familiarize users with the knowledge base. These might include demonstrations of key features, navigation tips, and best practices for finding information. Tailor training to different user groups, such as employees, customer support teams, or external clients, to ensure that everyone can effectively use the resource.
In addition to formal training, provide ongoing support and resources to ensure continued learning and growth. This might include user guides, FAQs, and contact information for assistance. Encourage feedback and address any challenges users may encounter.
Step 8: Monitor and Iterate
Regular monitoring involves tracking usage metrics, gathering feedback, and identifying areas for improvement. This step is essential for maintaining a knowledge base that meets the evolving needs of your organization.
Utilize analytics tools to track how your knowledge base is being used. Key metrics might include the number of searches, popular topics, and user engagement levels. Analyzing these metrics can provide valuable insights into user behavior and help identify content gaps or areas for improvement. Use this data to prioritize updates and enhancements.
Encourage user feedback through surveys or feedback forms. This direct input can reveal user challenges, preferences, and suggestions for improvement. Act on feedback by making necessary changes and enhancements. Iterative improvement ensures that your knowledge base remains relevant, user-friendly, and aligned with organizational goals.
Best Practices in Designing Your Knowledge Base
An internal knowledge base, when well-implemented, has a significant impact on internal efficiency. Companies that effectively leverage knowledge bases can improve internal team productivity by an average of 35% by streamlining access to information.
Designing a knowledge base goes far beyond simply compiling articles; it’s about crafting a dynamic and user-centric information hub that directly contributes to organizational success. Following best practices in its creation and ongoing management is paramount for enhancing its usability and overall effectiveness.
Here are some key considerations to keep in mind for maximizing your knowledge base’s value:
- User-centric design: Focus on the needs and preferences of your users. Design the layout and navigation with their experience in mind.
- Consistency: Maintain a consistent style and format throughout your knowledge base. This includes language, tone, and visual elements.
- Accessibility: Ensure your knowledge base is accessible to all users, including those with disabilities. This might involve providing alternative text for images and ensuring compatibility with screen readers.
- Search optimization: Optimize your content for searchability. Use relevant keywords and meta tags to improve search engine performance within your knowledge base.
- Feedback mechanisms: Implement mechanisms for user feedback and suggestions. This can help identify areas for improvement and enhance user satisfaction.
Incorporating these best practices means you can create a knowledge base that’s not just informative but also incredibly user-friendly and highly effective. You can transform your knowledge base into a dynamic asset, ensuring your team and customers can easily find the information they need, when they need it.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Knowledge Base Documentation
When establishing a knowledge base, it’s crucial to steer clear of common pitfalls that can severely hamper its effectiveness and adoption. Overlooking these mistakes can lead to a resource that is underutilized, unreliable, or even detrimental to organizational efficiency.
Gartner reports that 47% of digital workers struggle to find the necessary information for their jobs. This highlights the significant impact that design flaws and maintenance neglect can have on productivity and employee satisfaction.
Here are some critical mistakes to watch out for:
- Overloading with information: Avoid overwhelming users with too much information. Prioritize clarity and conciseness, focusing on essential content.
- Neglecting updates: Failing to regularly update your knowledge base can lead to outdated and incorrect information. Establish a process for continuous review and revision.
- Ignoring user feedback: User feedback is a valuable resource for improvement. Ignoring it can result in a knowledge base that doesn’t meet user needs.
- Lack of training and promotion: Without proper training and promotion, users may not fully utilize your knowledge base. Ensure that users are aware of its existence and know how to use it effectively.
- Poor navigation: Complicated navigation can hinder the user experience. Design a clear and intuitive knowledge base structure for easy information retrieval.
To forge a practical and user-friendly knowledge base, remember these common missteps. Addressing these pitfalls during development and ongoing management dramatically increases the likelihood of success. Neglecting them can lead to a resource that is underutilized, unreliable, and ultimately, a drain on organizational resources rather than a benefit.
Frequently Asked Questions: How to Organize a Knowledge Base
How do I create a knowledge base?
Creating a knowledge base involves several key steps, starting with defining your content strategy and understanding your audience’s needs. Next, choose a knowledge base builder, like Bloomfire. Then, organize and structure your information logically, employing clear hierarchies and user-friendly navigation. Finally, populate the knowledge base with well-written, accurate, and easily understandable content, utilizing various formats to enhance comprehension and engagement.
How often should I update my knowledge base?
You should update your knowledge base regularly, with the frequency depending on the dynamism of your information and user feedback. Aim for a proactive approach, reviewing and revising content whenever there are changes in products, services, policies, or common user queries. At a minimum, conduct a comprehensive audit and update at least annually to ensure all information remains accurate and relevant.
Can I incorporate multimedia elements into my knowledge base?
Yes, you can incorporate multimedia elements into your knowledge base to enhance understanding and engagement. For example, Bloomfire allows you to integrate various media types, such as videos demonstrating software functionalities, interactive diagrams, or audio files for quick tutorials. This rich media approach makes information more accessible and caters to different learning preferences, significantly improving the user experience.
Enhancing Your Organization with a Well-Structured Knowledge Base
Organizing your knowledge base enables you to build a powerful tool that significantly enhances organizational efficiency. Adhering to the steps in this guide helps you create a comprehensive resource, one that fully supports your company’s goals and meets user needs. Every aspect of knowledge management, from setting clear objectives to continuously monitoring and improving content, is crucial for your success.
Optimize Your Knowledge With AI
Use an AI-powered knowledge base for intelligent recommendations and seamless collaboration.
See Bloomfire in Action

How to Improve Customer Service: 9 Strategies to Automate Success

7 Best Customer Service Knowledge Management Systems in 2026

The 6 Knowledge Management Trends That Redefine Strategic Intelligence in 2026
Estimate the Value of Your Knowledge Assets
Use this calculator to see how enterprise intelligence can impact your bottom line. Choose areas of focus, and see tailored calculations that will give you a tangible ROI.

Take a self guided Tour
See Bloomfire in action across several potential configurations. Imagine the potential of your team when they stop searching and start finding critical knowledge.