10 Types of Knowledge Management Systems

Knowledge management systems (KMS) vary widely in their capabilities. They are tailored to meet strategic needs, addressing everything from the storage of formalized procedures to the capture of fluid, conversational expertise. They range from robust document repositories to dynamic, AI-powered collaboration platforms.
The right KMS choice depends entirely on the type of knowledge an organization needs to manage—whether it’s highly explicit (documented in manuals), deeply tacit (residing in employee experience), or somewhere in between. Below, we explore the various types of knowledge management systems, examples of how they are used in organizations, and their strategic value.
Summary
Knowledge management systems can be categorized into eight types:
- internal knowledge base
- external knowledge base
- document management system
- content management system
- collaboration platform
- learning management system
- expert system
- intranets and enterprise social networks
- social knowledge management system
- enterprise knowledge portals
What Are Knowledge Management Systems?
A knowledge management system is a cloud-based platform that stores and organizes information to improve efficiency, understanding, and alignment. Companies use knowledge management systems to consolidate information in one central source. They cater to multiple types of knowledge and information and how they are stored, including documents, videos, presentations, frequently asked questions (FAQs), audio files, and more.
The KMS is the primary location for shared information among employees instead of multiple systems (e.g., a company intranet, email, locally saved files, etc.). Employees can contribute information to the system, promoting streamlined knowledge management, knowledge retention, and continuous learning.
Your One-Stop KMS Is Here!
Explore Bloomfire’s diverse functionality for broader knowledge management activities.
Schedule a Consultation
What Are the Roles of Knowledge Management Systems in Businesses
The increasing demand for KMS proves its value across different levels of an organization to streamline several key functions. Employees waste approximately $2 million annually per 1,000 employees with average salaries of $60,000 because they spend 20% of their workday searching for information, highlighting the financial urgency of centralizing knowledge.
In North America, the adoption rate is notably high, with the region’s market share covering 40% of the global revenue. This trend underscores the competitive advantage of using a knowledge management system to improve productivity and foster a culture of continuous improvement and knowledge sharing. Specifically, KMS plays the following roles in a business:
1. Seamless onboarding of employees
Organizations can significantly speed up onboarding by providing new hires with immediate access to all necessary resources about the company, its products, and its policies. This approach makes new employees feel welcomed and prepared, enhancing their productivity. In a study of Bloomfire customers, we found that 93% of our respondents had improved their onboarding time since implementing Bloomfire.
2. Enhancing internal communications
Knowledge management systems can centralize companies’ communications, ensuring that important updates are not lost in transit. Systems like Bloomfire excel in this area by allowing users to customize homepages and facilitate automatic notifications.
Bloomfire integrates seamlessly with popular communication tools such as Slack and Microsoft Teams, enabling organizations to set up automated notifications that keep everyone informed and engaged across multiple platforms.
3. Streamlining customer service
Customer service teams can use a knowledge management system to put answers to customers’ questions at their agents’ fingertips. Companies can reduce the time CS teams spend searching for knowledge by up to 35%. When a customer calls (or chats with) an agent, the agent can perform a quick keyword search in the knowledge management platform to find relevant, approved information they can use to assist the customer.
4. Facilitating On-Demand Training
Knowledge management systems provide versatile platforms that enable employees to access training materials at their convenience — a seamless integration of learning into their daily workflow. This asynchronous approach complements formal training sessions by allowing employees to use training resources, such as video tutorials, how-to guides, and FAQs, whenever needed.
Centralized in a knowledge management system, these resources are easily accessible and can be broken down into bite-sized components. This makes it easier for employees to digest and apply new knowledge without disrupting productivity. This method enhances learning flexibility and ensures that training is continuously available, supporting ongoing professional development across the organization.
What Are the Two Major Types of Knowledge Management Systems?
While there are numerous types of Knowledge Management Systems, they can broadly be categorized into two major types: explicit knowledge management systems and tacit knowledge management systems.
a. Explicit knowledge management system
This knowledge management system type focuses on capturing and managing knowledge that can be easily documented, such as procedures, manuals, and reports. These systems are designed to store and retrieve structured information, making it accessible and reusable. By organizing explicit knowledge, these systems help standardize processes and improve operational efficiency.
b. Tacit knowledge management system
A tacit KMS captures informal knowledge, such as personal experiences, insights, and skills. These systems facilitate knowledge sharing through social interactions, mentorship, and collaboration. By enabling the exchange of tacit knowledge, organizations can foster innovation and creativity.
Differentiating these two major types of knowledge management systems is crucial for addressing the diverse knowledge needs within your organization. It is also noteworthy to understand that combining both allows you to create a comprehensive knowledge management strategy that supports explicit and tacit knowledge sharing.
What Are The Specific Types of Knowledge Management Systems?
Knowledge management systems are diverse tools and platforms that capture, organize, and distribute knowledge within an organization or to its customers. These systems range from internal repositories to collaborative platforms that facilitate the sharing of tacit knowledge through communication and teamwork. The following are the specific types of knowledge management systems:

1. Internal Knowledge Bases
Internal knowledge bases (IKBs) are critical components within a comprehensive knowledge management ecosystem. Functionally, they serve as centralized hubs designed to orchestrate accumulating and utilizing an organization’s proprietary knowledge. They facilitate the transformation of tacit knowledge into explicit, readily accessible information, thereby enhancing operational efficiency and decision-making.
Architecturally, they often structure data using relational or graph databases, enabling complex queries and knowledge retrieval. They also incorporate features such as semantic search, which uses natural language processing (NLP) to understand user intent.
Common examples of IKB providers include Atlassian Confluence, Notion, Microsoft SharePoint, and Guru, all of which offer robust features like collaborative editing and search capabilities. If you’re looking for an artificial intelligence (AI) cloud-based knowledge management platform with internal and external knowledge bases for enterprise, check out Bloomfire. It goes beyond centralizing knowledge and connecting it to help form Enterprise Intelligence.
2. External Knowledge Bases
External knowledge bases are publicly accessible information repositories that empower users outside the organization. These knowledge management systems deliver explicit knowledge, often structured as FAQs, troubleshooting guides, and product documentation. They aim to facilitate self-service support and reduce reliance on direct interaction.
Furthermore, their integration with customer relationship management (CRM) systems allows for personalized content delivery and contextual support, enhancing customer satisfaction. Because they cater primarily to customers, the system must have rigorous content governance and maintenance, ensuring accuracy and relevance for a diverse user base.
External knowledge base solutions are widely provided by customer support platforms like Zendesk Guide, Freshdesk, and Help Scout, or standalone documentation tools like Document360 and Helpjuice. Companies like Canva and Spotify offer excellent real-world examples of well-structured, user-friendly external knowledge bases tailored for customer self-service.
3. Document Management Systems
While internal knowledge bases serve as warehouses of data or information, document management systems (DMSs) take a step further by implementing more granular access controls and sophisticated search functionalities. A DMS is a type of knowledge management system that primarily concentrates on document lifecycle management. It employs metadata tagging, version control, and access control lists (ACLs) to ensure data integrity and security.
DMSs are centered on explicit, structured information. This includes features like optical character recognition (OCR) for text extraction, indexing for rapid searching, and workflow automation for document routing and approvals. Prominent document management systems providers include cloud storage leaders like Box and Google Workspace, which offer powerful organizational features suitable for DMS use.
4. Content Management Systems
Content Management Systems (CMS) occupy a specialized niche within the broader landscape of knowledge management systems. They focus on the creation, modification, and publication of digital content. CMSs provide authoring and version control tools through databases and templating engines, allowing consistent formatting and efficient updates across various channels.
Their strength lies in the dynamic delivery of information, supporting complex content relationships and metadata management, which is vital for large-scale knowledge repositories. This capability differentiates them from basic file-sharing platforms or communication tools, making them essential for organizations requiring sophisticated management of their digital knowledge assets.
Common examples of CMS providers include open-source options like WordPress and Drupal. Enterprise solutions include Adobe Experience Manager and HubSpot Content Hub.
5. Collaboration Platforms
Unlike static repositories such as traditional document management systems, collaboration platforms leverage real-time communication, shared workspaces, and integrated applications to foster enterprise intelligence. They often incorporate features like asynchronous and synchronous communication channels (e.g., chat, video conferencing), file versioning with concurrent editing capabilities, and API integrations with other enterprise applications.
Like other types of knowledge management technologies, collaboration platforms emphasize social interaction and emergent knowledge. Integrating features like @mentions, threaded conversations, and shared calendars enhances contextual awareness and facilitates seamless knowledge transfer. For instance, Microsoft Teams acts as a central hub where projects, documents, and communications converge.
Similarly, Slack facilitates immediate, topic-based knowledge transfer through channels and searchable message history. It preserves conversational expertise that might otherwise be lost in email chains.
6. Learning Management Systems
Learning Management Systems (LMS) are specialized knowledge management platforms that facilitate creating, delivering, and tracking educational and training content. Their emphasis on formalized learning experiences and robust analytics capabilities distinguishes them from broader knowledge repositories or collaboration tools.
An LMS provides a structured environment for managing learning resources, including course materials, assessments, and progress tracking. It enables organizations to systematically manage and deliver training programs, monitor learner performance, and measure the effectiveness of educational initiatives.
Popular LMS providers for corporate training and education include Docebo, Cornerstone OnDemand, TalentLMS, Moodle, and SAP Litmos. They offer features ranging from robust compliance tracking and enterprise-level scalability to simple, collaborative course creation.
7. Expert Systems
A relatively new type of KMS, Expert Systems are a distinct category within knowledge management, leveraging artificial intelligence to emulate the decision-making capabilities of human experts. These systems operate through a knowledge base containing domain-specific facts and rules and an inference engine that applies these rules to user-provided data.
In addition, expert systems typically employ frame-based systems or case-based reasoning and are often implemented using programming languages such as Prolog or Lisp. Examples of this knowledge management system type include medical diagnostic systems, financial risk assessment tools, and automated troubleshooting systems.
Modern expert systems, now often integrated as Intelligent Techniques within larger platforms, are provided by major tech firms like IBM (with Watson/watsonx for healthcare and finance), and embedded in solutions from vendors like SAP, Oracle, and Salesforce. Historically significant, dedicated examples include the medical diagnostic system MYCIN and the computer configuration system XCON.
8. Intranets and Enterprise Social Networks (ESN)
Intranets and enterprise social networks (ESNs) foster organizational-wide communication and knowledge diffusion. They typically feature capabilities such as news feeds, document repositories, discussion forums, and employee directories, facilitating formal and informal knowledge exchange.
What distinguishes Intranets and ESNs from general collaboration platforms is their emphasis on establishing a cohesive organizational culture and promoting a sense of community. Collaboration platforms facilitate team-specific communication and project-based collaboration through features like real-time messaging and file sharing. Meanwhile, Intranets/ESNs connect employees across departments and geographical locations. This intranet advantage helps break down information silos and promote cross-functional knowledge sharing.
Common examples of these platforms include Microsoft Viva Engage (formerly Yammer), which offers a central hub for documents and social interaction across the enterprise. Other popular providers include Jive, Happeo, and Workvivo, which are designed to be mobile-friendly, culture-building social intranet solutions.
9. Social Knowledge Management Systems
Social Knowledge Management Systems (SKMS) focus specifically on capturing and leveraging the vast amount of tacit knowledge and expertise that lives within employee relationships and daily conversations. These systems move beyond simply storing documents to actively encouraging and structuring social interaction, treating communication itself as a key knowledge asset.
Functionally, SKMS are built around community features like Q&A forums, employee expertise directories, blogs, and wikis. Their primary objective is to facilitate peer-to-peer knowledge transfer, making it easy for an employee to find not just a document, but the person who holds the crucial, uncodified expertise.
AI often plays a key role here, using machine learning to map expertise across the organization and suggest the most relevant expert or discussion thread for a given question. Popular examples include platforms with strong community features, such as Stack Overflow for Teams, Quip, which surface bite-sized, validated knowledge snippets directly into employees’ workflows.
10. Enterprise Knowledge Portals
Enterprise Knowledge Portals (EKPs) represent the ultimate goal of the knowledge management hierarchy, acting as a single, personalized gateway to all of an organization’s internal and external information systems. An EKP is not a separate storage system but rather an integration layer that pulls together content from various underlying KMS types into a unified, user-friendly interface.
The primary advantage of an EKP is its ability to deliver contextualized and personalized knowledge. This function relies heavily on federated search, which can query multiple data sources simultaneously and apply advanced filters or AI-driven relevance ranking.
Bloomfire serves as a prime example in this space, acting as an AI-powered knowledge management platform designed not merely to store knowledge, but to pull actionable insights and solidify Enterprise Intelligence. It achieves this through robust integrations and specialized knowledge connectors that link to diverse enterprise applications and data sources.
6 Concrete Examples of Knowledge Management Systems in Organizations
Knowledge management systems have various real-world applications, each tailored to specific needs. For instance, Bloomfire is a robust internal knowledge base for collaborative documentation, while Zendesk Knowledge empowers customer self-service through comprehensive support articles. LMSs like Moodle facilitate online training and development, and collaboration tools like Slack and Microsoft Teams enable real-time knowledge sharing within teams.
These platforms offer features that cater to your KM goals. However, implementing a KMS should begin by knowing how you want to use the system. Otherwise, employees may miss out on the benefits of knowledge management altogether–a fact exhibited by IDC research, in which only 45% of large-sized company employees use KMS diligently.
The following examples demonstrate how organizations leverage this technology to manage valuable knowledge.
1. Internal Search Engine
An internal search engine is a specialized tool for organizations that indexes and retrieves information from a company’s internal data sources. Unlike public search engines that crawl the Internet, these systems focus on documents, databases, communication platforms, and other repositories within the organization’s network. The goal is to provide employees with quick and accurate access to internal knowledge, improving productivity and decision-making.
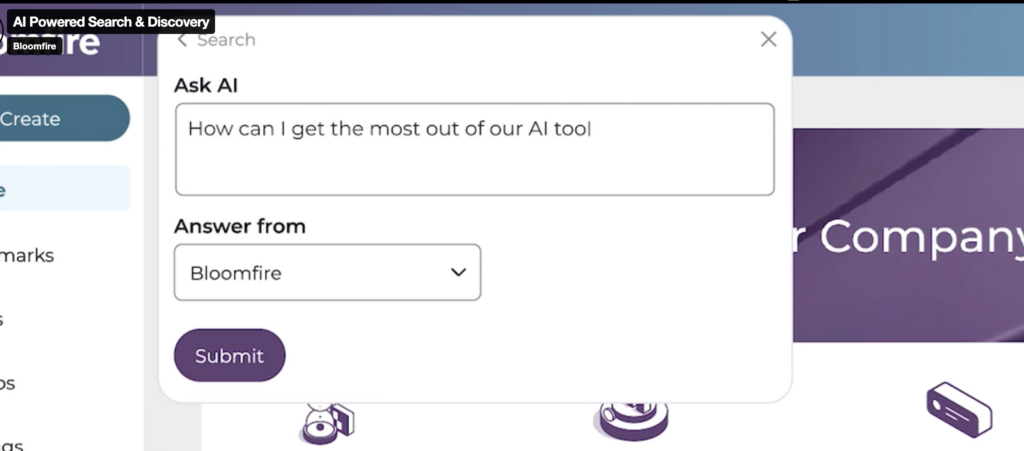
Bloomfire is an excellent example of a KMS with robust capabilities for internal search engines. Its intuitive interface and powerful search capabilities allow employees to find relevant information across various content types efficiently. Notably, Bloomfire leverages AI to enhance search accuracy. Its AI capabilities can analyze content, identify patterns, and understand user intent, leading to more efficient and effective knowledge retrieval.
2. Online Community Forums
An online community forum is a website where visitors with a shared interest or area of expertise can ask and answer one another’s questions and share feedback or recommendations. They help businesses keep customers engaged and happy, generate content from their biggest advocates, conduct market research, and innovate their products based on user feedback.
In some cases, brands will create an online forum for their customers or fans to network and provide peer-to-peer support. Examples of branded community forums include Underlined, Penguin Random House’s platform for writers and book lovers, and Community Center, Airbnb’s forum for verified hosts to share knowledge, get inspired, and network.
3. Enterprise Learning Management Systems (LMS)
As mentioned above, learning management systems focus on housing, distributing, and tracking engagement with learning and training materials. However, an enterprise LMS is more specific to internal business use. It allows employees to access learning materials from anywhere on demand. Businesses can use the system to upskill employees efficiently, onboard new hires faster, hold employees accountable for staying up-to-date with training, and increase job satisfaction.
You can maximize various features to match your employees’ learning styles. These include interactive quizzes, engagement analytics, customizable learning paths, and course creation and management tools. Examples of LMS software solutions include Seismic and Moodle.
4. Customer Service Knowledge Bases
Customer support knowledge bases consolidate customer-facing information and FAQs and make them easy to access. With the right KMS for a customer service knowledge base, you can increase customer satisfaction and loyalty and reduce the average time to resolve customer issues.
These knowledge bases can be internal or external. They can be employee-only systems that allow service representatives to quickly locate information and assist customers, or they can be customer-facing websites that empower customers to help themselves by finding answers to common questions.
Did You Know?
Bloomfire is a platform that can be used as an internal and external knowledge base. You can read about how businesses like Orvis use Bloomfire to connect their associates with product and customer knowledge. Check out our Help Center for an example of an external knowledge base.
5. Research and Insight Libraries
Research and insights libraries are cloud-based platforms that serve as repositories for market research and consumer insights materials. These platforms typically house diverse content, including research reports, slide decks, industry news, customer interview recordings, and secondary vendor research. These platforms also minimize redundant research efforts by enabling all teams to view existing materials, thus fostering increased communication and engagement with valuable insights across all research sources.
Many organizations maintain separate libraries—one for finalized content ready to be shared with stakeholders and another for raw materials like video recordings, which are more accessible for research teams to analyze. Bloomfire enhances these libraries with advanced video transcription features, making spoken words within videos searchable. This capability allows users to efficiently locate and review critical moments in customer interviews, helping to quickly identify and act on emerging trends.
6. Company-Wide Knowledge Management Systems
Companies possess a vast trove of knowledge and insights, which often become siloed within teams or departments. Company-wide knowledge management systems distribute knowledge across an entire organization, so everyone has one place to find the information to do their jobs. Because these platforms contain large volumes of knowledge in many different formats, they must have:
- A one-stop, powerful search engine
- The ability to tailor the way information is structured (e.g., creating custom categories and sub-categories)
- The ability to easily create and update content (with no coding required)
- Permission controls for department-specific or sensitive content access
- The ability to automate maintenance processes and make updates to content in bulk
Due to the configurable and scalable nature of Bloomfire, the platform supports cross-department or company-wide knowledge management for many customers, including Insperity, Dominion Energy, and Dime Community Bank.
One of the most significant benefits of a company-wide knowledge management system is that it allows an organization to maximize the value of its collective intelligence. It can reduce employees’ time searching for information, prevent knowledge loss, amplify subject matter expertise, keep teams aligned, and empower everyone to do impactful work.
Empowering Your Organization with the Right Knowledge Management System
There are many types of knowledge management applications, each designed to enhance specific aspects of organizational efficiency and intelligence sharing. Choosing the right knowledge management system is crucial for leveraging the full potential of your organization’s collective intelligence. By understanding these various systems and their applications, you can select a solution that not only meets your current operational needs but also supports your long-term strategic goals.
Select the Right KM Solution
Download our free, comprehensive Ultimate Guide to Knowledge Management and Top Software Platforms.
Get Yours Now
Knowledge management systems are utilized by nearly every stakeholder connected to an organization’s intellectual assets. Internally, this includes all employees and departments to boost collective efficiency and innovation. Externally, the systems are used by customers and partners through public-facing knowledge bases, enabling self-service for support, product information, and troubleshooting.
Information management (IM) focuses on the technical processes of acquiring, structuring, storing, and securing explicit data and documents. In contrast, knowledge management (KM) is a broader, people-centric discipline that utilizes information to capture, share, and apply both explicit and tacit knowledge, thereby fostering innovation and driving better organizational decisions.
An organization should choose a KMS by first identifying its specific knowledge needs (e.g., internal troubleshooting, customer self-service, or expertise sharing) and assessing the type of knowledge that is most critical: explicit or tacit. The best system should then be selected based on its ability to support these goals, integrate with existing enterprise tools, and provide robust search functionality.
Enterprise-wide knowledge management systems are umbrella platforms that consolidate various tools like internal knowledge bases, document management systems, and collaborative workspaces to ensure consistent knowledge across all departments. Platforms like Bloomfire exemplify this type, focusing on centralizing disparate data and insights with AI-powered search to eliminate organizational silos and create a unified layer of Enterprise Intelligence.
Knowledge management systems are used by virtually all types of businesses, ranging from large enterprises and global corporations (e.g., tech, finance, healthcare) to small and medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs). Their adoption is driven by the need to manage internal complexity, support a dispersed workforce, and deliver efficient customer service across every industry.
The essential features of a knowledge management system include robust search and retrieval capabilities (often enhanced with AI) and a centralized repository for storing content like FAQs, guides, and policies. Key functional components also encompass authoring and collaboration tools for content creation, version control to ensure information accuracy, and analytics to track content usage and identify knowledge gaps.

Enterprise AI Search: Definition, Benefits, and Evolution

The Benefit of Company-Wide Knowledge Management in 2026

Are You Making These Common Knowledge Sharing Mistakes?
Estimate the Value of Your Knowledge Assets
Use this calculator to see how enterprise intelligence can impact your bottom line. Choose areas of focus, and see tailored calculations that will give you a tangible ROI.

Take a self guided Tour
See Bloomfire in action across several potential configurations. Imagine the potential of your team when they stop searching and start finding critical knowledge.